Since its release in 2003, WordPress has transformed from a simple blogging tool to a comprehensive system for building websites. This transformation included many changes to its user interface (UI), which made it easier to use and more versatile for various types of websites.
In this article, we will examine how the WordPress UI has evolved over the years, starting with the early versions and moving on to the latest updates. We will highlight the key changes that have made WordPress a top choice for website creators worldwide.
This journey through the WordPress UI evolution will show how each update has made it more user-friendly and capable of handling different kinds of web projects.

The Beginning of WordPress
WordPress started out in 2003. This was mainly because the development of an already popular blogging software called b2/cafelog was discontinued by its main developers.
Two passionate users of b2/cafelog, Matt Mullenweg and Mike Little, decided to build a new platform on top of that blogging software. This is how WordPress was first released on May 27, 2003. You can learn more about the origin story of WordPress in our article on the history of WordPress.
Since then, there have been a lot of WordPress releases. In this article, we will highlight the releases that introduced a big change in the admin panel user interface.
WordPress 0.71 – (June 2003)
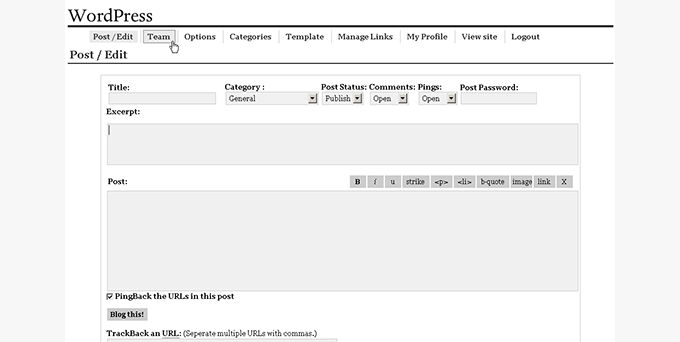
The landing page of the WordPress 0.71 admin panel was used to write blog posts directly. It didn’t really have many options outside the post-editor interface.
It was kept simple by including fewer features. For instance, users could only assign one category to each post.
It also had a tedious installation method where a lot of information was changed manually by editing the core files of the software.
WordPress 1.0.1 (Miles – 2004)
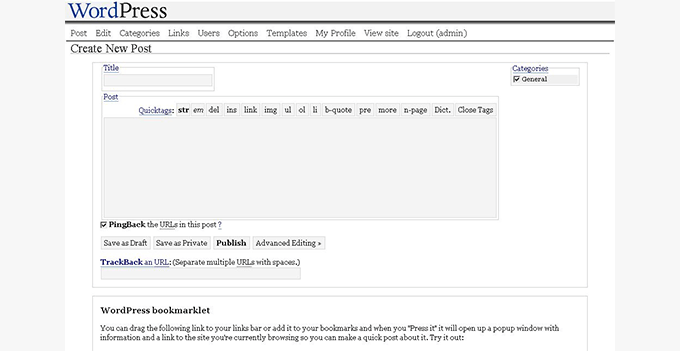
WordPress started naming its major releases after Jazz musicians with the release of version 1.0.1. As you can see, this release was named after a famous musician, Miles Davis.
In this version, WordPress stopped using the b2 file structure and moved toward its own style of filing structure.
New features included multiple category selections, an SEO-friendly URL structure, comment moderation, a new installer, and several other improvements.
WordPress 1.2 – Mingus (May 2004)
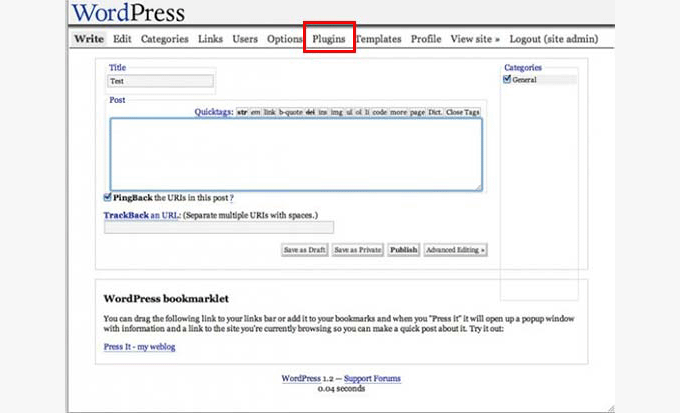
Named after Charles Mingus, WordPress 1.2 was a monumental release. One of the most important upgrades in this version was the introduction of ‘Plugins’, which are now a staple of the WordPress ecosystem.
Other notable changes were subcategories, custom fields, thumbnail creation, post preview, encrypted passwords, and the ability to ping more than one service at a time.
WordPress 1.5 – Strayhorn (Feb 2005)
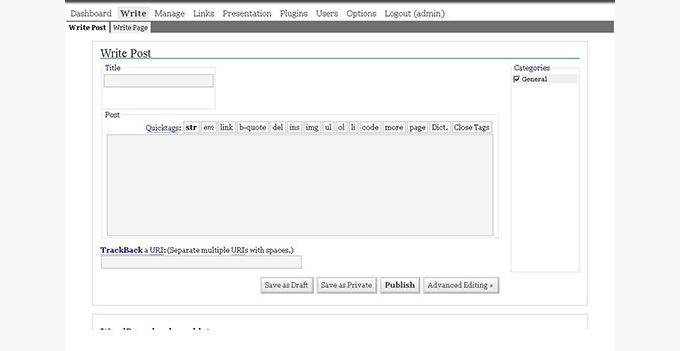
This version of WordPress was named after Billy Strayhorn. It showed the first glimpse of a new dashboard style. It didn’t use Ajax and was way slower than the WordPress we use today.
Another significant feature was the introduction of pages alongside posts, allowing users to create static pages not part of their blog feeds. This release also supported installing multiple themes in a single WordPress installation.
WordPress 2.0 – Duke (Dec 2005)
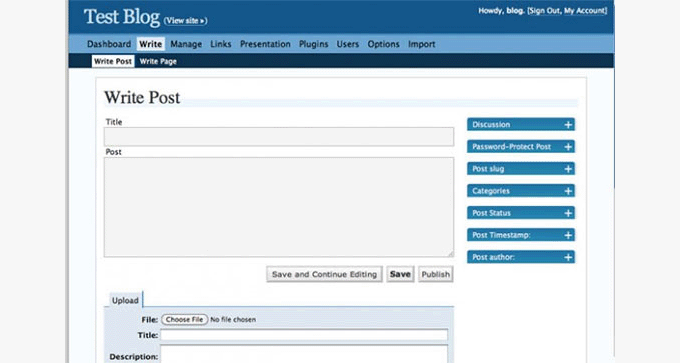
WordPress 2.0 brought a major overhaul of the WordPress admin interface. It had a large blue header on top and a completely reimagined admin area.
It was way faster than previous releases, as it used Ajax to perform certain tasks. This release also included a full WYSIWYG editor.
Akismet was introduced as a plugin to combat the growing comment spam problem. Some other notable features were image/file uploading, theme preview via thumbnail (screenshot.png), improved posting speed, new hooks for developers, and more.
WordPress 2.1 – Ella (Jan 2007)
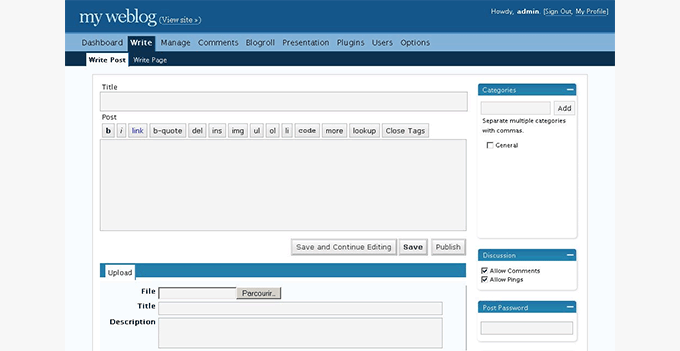
WordPress 2.1 Ella was the first release to introduce a new admin screen to manage comments.
The comment management process was significantly improved because users could delete or approve comments without reloading admin screens.
WordPress 2.3 – Dexter (Sep 2007)
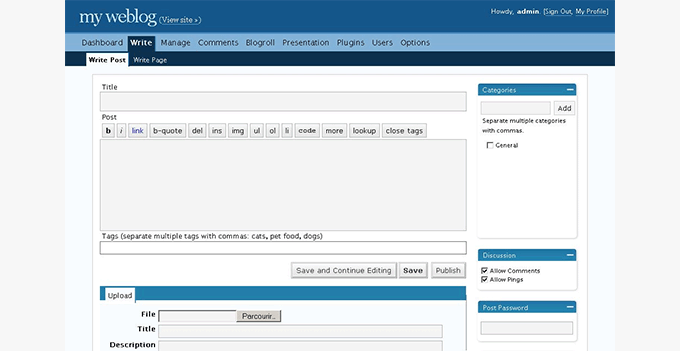
This release didn’t drastically change the WordPress user interface but added several significant improvements. For the first time, WordPress improved native support to add tags to your posts.
It also introduced an update notification system, which allowed WordPress core and plugins to show notifications when a new version was available.
This release also started auto-redirecting users to the correct WordPress URL as defined in the settings.
WordPress 2.5 – Brecker (Mar 2008)
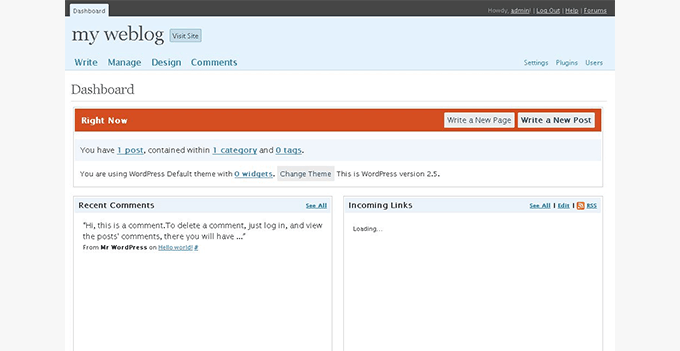
For WordPress 2.5, the WordPress team collaborated with Happy Cog, a leading web design consultancy firm, to redesign the WordPress admin user interface.
It was a major design improvement, and it had a huge impact on how we use WordPress today.
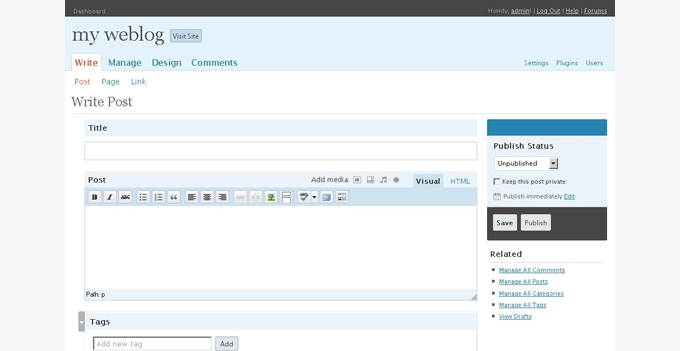
The dashboard got much better as they added more useful information there. This was the first version where we saw a one-click upgrade for plugins in the WordPress plugin directory.
A much better visual editor and a built-in gallery were also included in this release.
Many of the core components of this redesign are still a major part of the software. However, its appearance quickly changed just 10 months later.
WordPress 2.7 – Coltrane (Dec 2008)
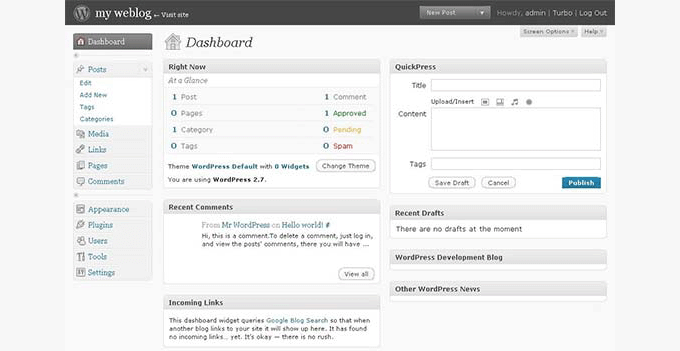
WordPress 2.7 brought another major upgrade to the WordPress admin user interface. Users were now able to readjust WordPress dashboard elements. Screen options were introduced so that users could show and hide elements to meet their requirements.
Other notable features included easier plugin installation through the WordPress admin panel, admins could add comment replies from the admin panel, threaded comments, sticky posts, keyboard shortcuts, comment pagination, and more.
WordPress 2.9 – Carmen (Dec 2009)
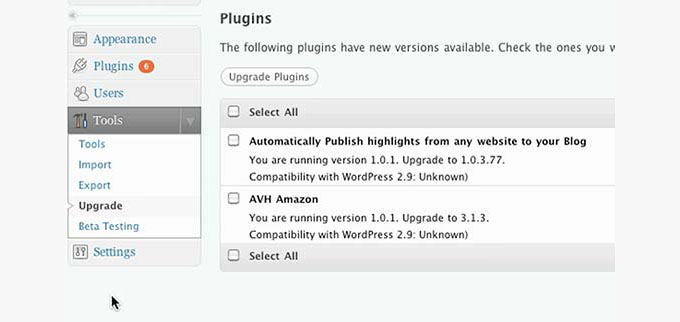
WordPress 2.9 didn’t change the user interface, but it did add several new features that integrated beautifully into the existing WordPress interface. One of these changes was a plugin update system that allowed users to update their plugins to the more recent versions with a single click.
Another major change in the release was image editing features, which allowed users to crop, resize, rotate, scale, and flip images in WordPress.
WordPress 3.0 – Thelonious (2010)
WordPress 3.0 Thelonious was a major upgrade that truly transformed WordPress from a blogging platform to a full-fledged CMS.
It introduced post types, taxonomies, custom backgrounds, headers, shortlinks, and navigation menus. It also came with a new default theme called Twenty Ten, which started the tradition of introducing a new default theme every year that is named after the year itself.
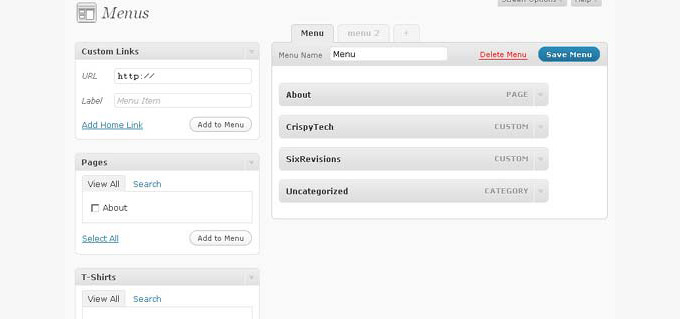
This release merged a WordPress sister project called WordPress MU into core WordPress. This feature is now known as WordPress multisite. The admin interface’s basic style could adapt to all these major changes without another significant overhaul of the admin area.
WordPress 3.1 – Django Reinhardt (2011)
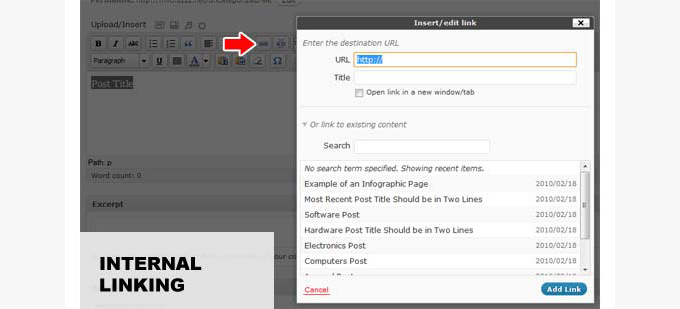
WordPress 3.1 continued adding features to the robust WordPress user interface.
With this new release, WordPress introduced the admin bar, post formats, and a better internal linking feature.
WordPress 3.3 – Sonny (2011)
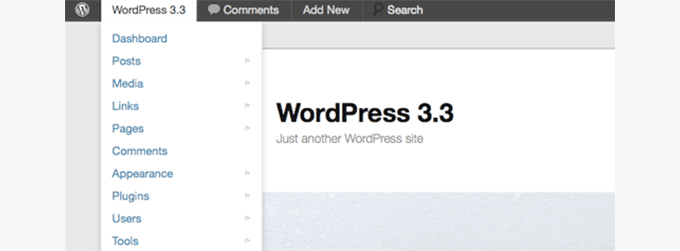
Released in December of 2011, WordPress 3.3 came packed with features and improvements to the existing WordPress UI.
It added fly-out menus for better navigation in the admin area, a revamped admin bar, drag and drop to upload media files, and tool tips. You can see more features and screenshots of WordPress 3.3.
WordPress 3.5 – Elvin (2012)
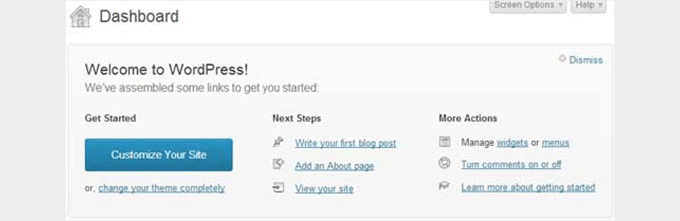
Mobile and high-resolution devices were already becoming accessible to all users. WordPress 3.5 streamlined the user interface for modern retina display devices.
This release included upgraded icons and adaptive styles that looked great on any screen resolution. See more features and screenshots of WordPress 3.5.
WordPress 3.8 – Parker (2013)
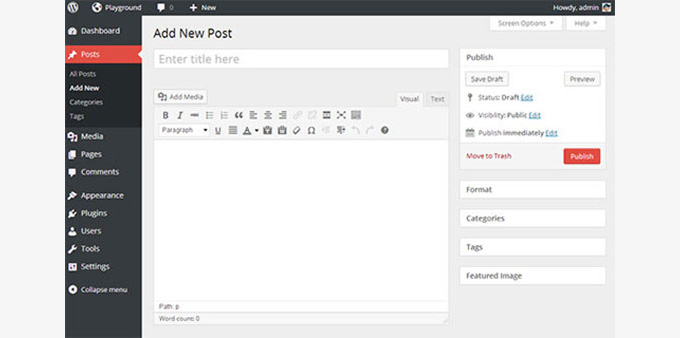
The appearance and the basic style of WordPress UI hadn’t been changed since 2008 and were way overdue for a major upgrade.
This upgrade aimed to handle mobile devices more elegantly and make WordPress more accessible. After a ton of work, the new WordPress user interface was released with WordPress 3.8.
The new user interface, which is still used (with minor enhancements), was mobile responsive, had more color schemes, had icon fonts used in the dashboard, and used the Open Sans font for typography.
WordPress 3.9 – Smith (2014)
WordPress 3.9 made several enhancements to extend the user interface for new features.
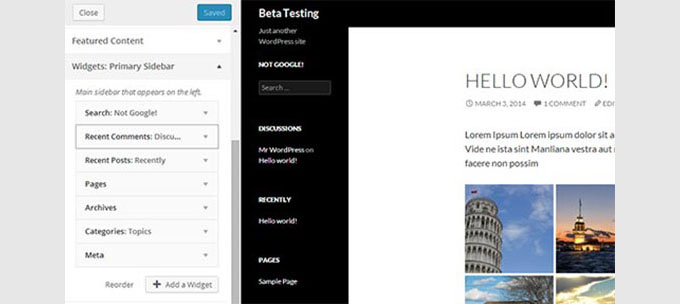
It started using flat buttons in the post editor, drag-and-drop image uploads, gallery previews, and more.
It also added live previews when adding widgets in the theme customizer. See more features and screenshots of WordPress 3.9.
WordPress 4.0 – Benny (2014)
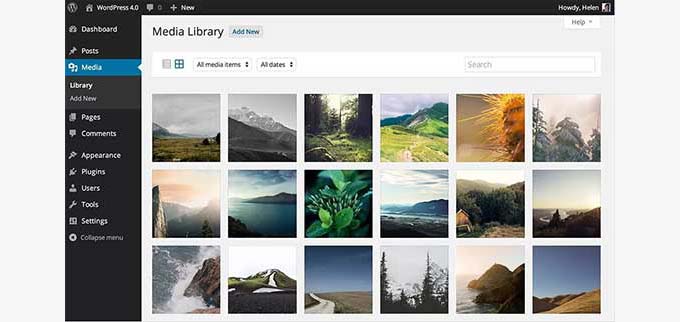
That very same year, WordPress 4.0 was released. There were no major changes to the UI. However, there were some cool changes that extended the existing WordPress admin interface.
A new grid view for the Media gallery was introduced with infinite scroll and smooth editing. See screenshots and features of WordPress 4.0.
WordPress 4.2 – Powell (2015)
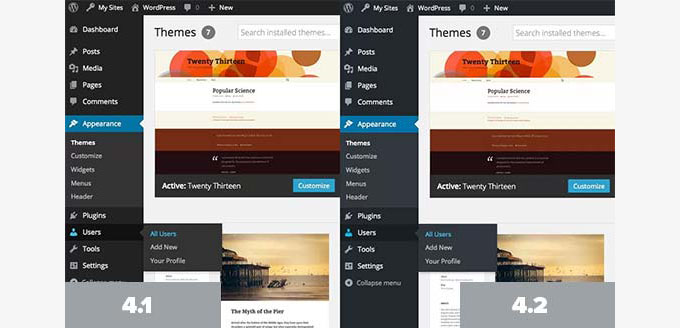
WordPress 4.2 came with a tiny but significant improvement in the admin area color scheme.
The grays were given a slight blue hue, and the blues were changed to pure blue with no red channel. See more features and screenshots of WordPress 4.2.
WordPress 4.5 – Coleman (2016)
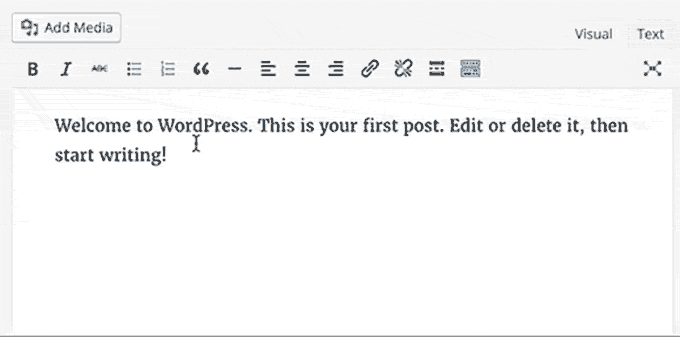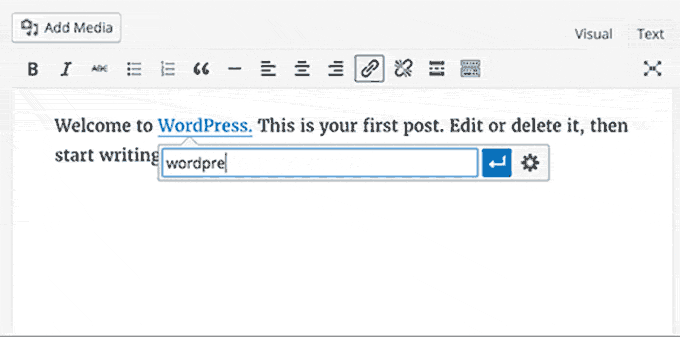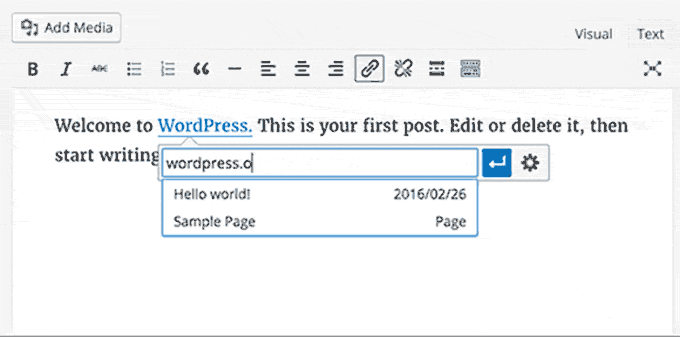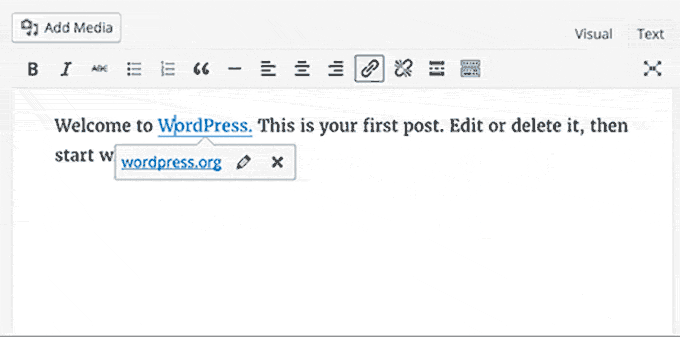
WordPress 4.5 brought some much-needed improvements to the default WordPress post editor. A new inline link editing feature and some new inline text shortcuts were introduced.
Responsive previews were added in the theme customizer, allowing users to preview their theme for desktop, tablet, and mobile screens without changing devices. For more features, see our article on the release of WordPress 4.5 with screenshots.
WordPress 4.6 – Pepper (2016)
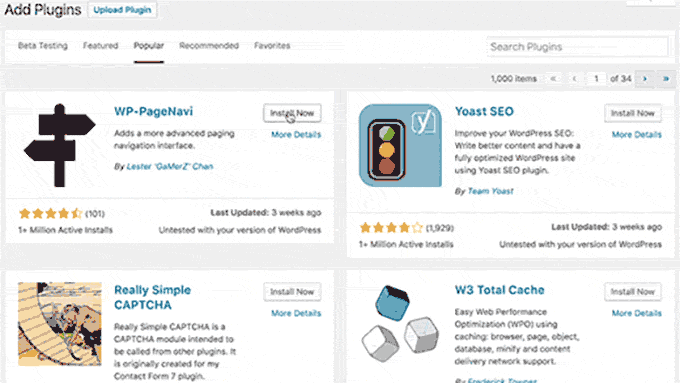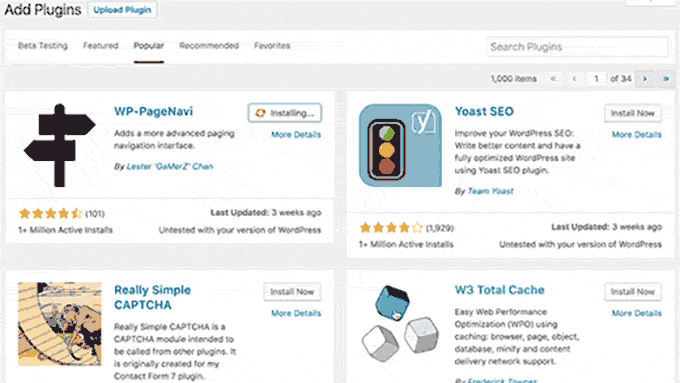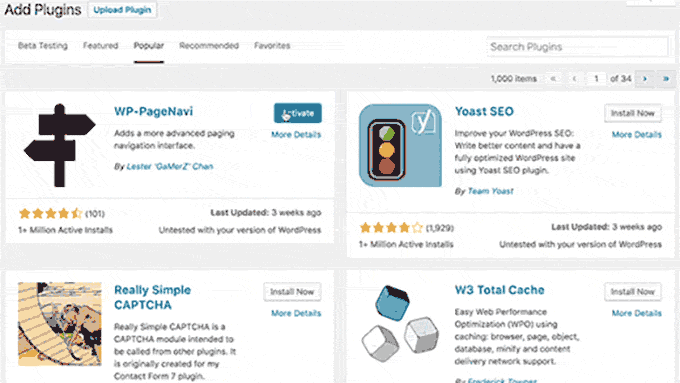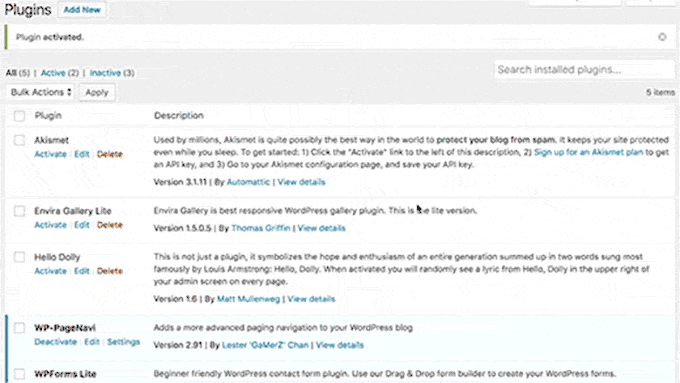
With WordPress 4.6, the core team decided to start using native fonts instead of loading Open Sans from Google servers.
This release also streamlined updates, which allowed users to install, update, and delete plugins/themes without reloading the page.
WordPress 4.8 – Vaughan (2017)
WordPress 4.8 introduced a new set of widgets to add media like images, audio, video, and rich text.
It also added a new dashboard widget that displayed WordPress news and events. For more features and screenshots, see our overview of WordPress 4.8.
WordPress 4.9 – Tipton (2017)
The last major release of WordPress for 2017 added more features to the theme customizer, including a new theme browsing and preview experience.
It also added syntax highlighting and auto-completion to code editors for custom CSS and theme/plugin editors.
WordPress 5.0 – Bebo (2018)
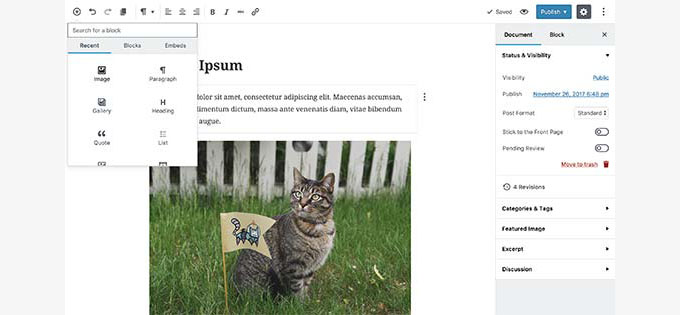
WordPress 5.0 was released in December 2018. It was a major milestone that introduced a new block-based editor codenamed Gutenberg.
The new block editor allowed users to easily create beautiful content layouts with an intuitive new interface. Each content element was added as a block with its own settings, and users could save and reuse blocks for much faster writing.
The new block editor didn’t have as many features as a full-featured WordPress page builder, but it laid the groundwork to use the same block editor functionality in other areas of WordPress.
You can see our post on Gutenberg vs. WordPress page builders for a full breakdown of the differences in the new content editor.
It was a massive shift from the plain old TinyMCE editor to a more modern editor. Users who were not ready for the transition were able to use the old editor by installing the Classic Editor plugin.
However, many experts, including WPBeginner, believed that it was a necessary step forward for WordPress. The old classic editor interface felt way outdated compared to the other popular website builders on the market.
WordPress 5.2 – Jaco (2019)
In 2019, WordPress remained focused on improving the block editor by adding new features, fixing bugs, and enhancing user experience.
With WordPress 5.2, a recovery mode feature was introduced. Instead of showing a fatal error, WordPress displayed an error page.
It also emailed website administrators with a link to access the admin area under recovery mode.
This allowed site owners to quickly fix the issue without going through several troubleshooting steps.
WordPress 5.4 – Adderley (2020)
The block editor remained the most important part of WordPress development in 2020 as well. With each release, it kept improving with new blocks and tools and a much faster experience.
With WordPress 5.4, the full-screen editor became the default setting for the block editor.
The block editor also introduced a new toolbar for mobile screens.
This allowed users to have a much cleaner editing experience on smaller screen sizes.
WordPress 5.5 – Eckstine (2020)
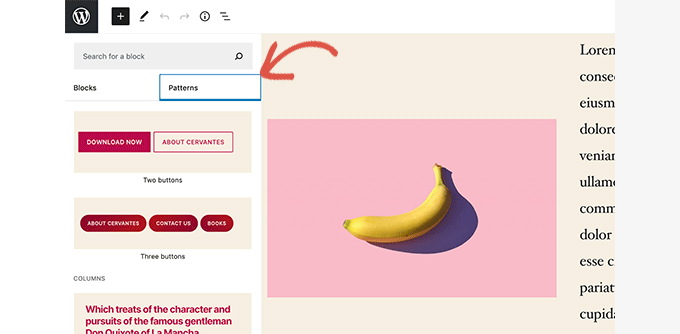
WordPress 5.5 introduced block patterns.
A pattern is a set of blocks pre-arranged to quickly add commonly used design elements like headers, footers, intros, calls to action, and more.
WordPress 5.8 – Tatum (2021)
Over the last few years, WordPress has continued to improve the block editor in an effort to offer a full site editing solution.
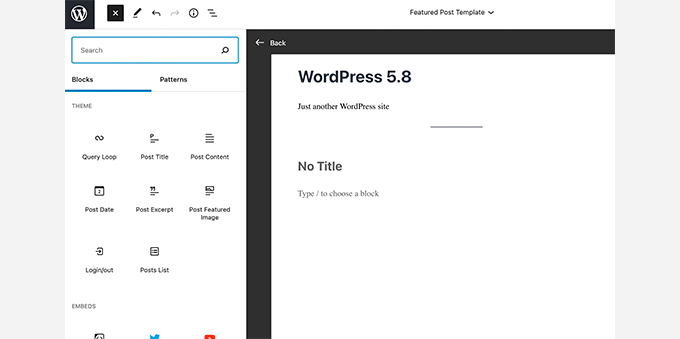
In WordPress 5.8, a new templates feature was introduced along with several site-wide blocks to help you easily create site-wide templates in WordPress.
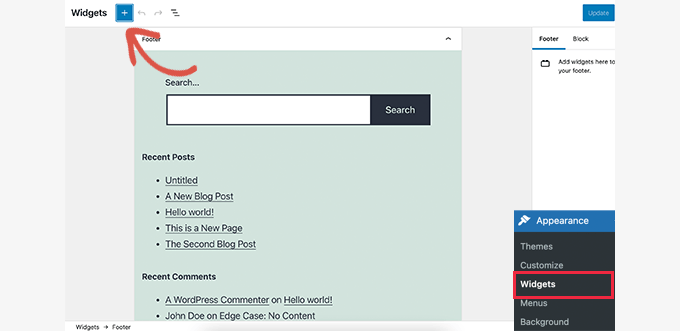
This version also introduced block-based widgets. Each widget-ready area in your WordPress theme now appeared as a tab in the block editor. Users were able to add widgets as blocks to their websites’ sidebars and widget-enabled areas.
These features laid the groundwork for future updates and prepared WordPress to use a block-based site editor.
WordPress 5.9 – Josephine (2022)
WordPress 5.9 arrived in January 2022, with the full site editor making its debut.
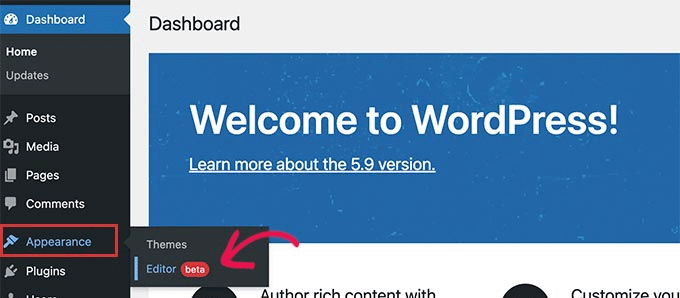
It replaced navigation menus, widgets, and theme customizer links from the admin sidebar with a link to the site editor.
However, it was only visible to users with a block-based theme activated on their sites. The release came with Twenty Twenty-Two as the new default theme with full support for the site editor.
The site editor used the block editor, so it provided the same user interface for editing websites that users were already using for writing content.
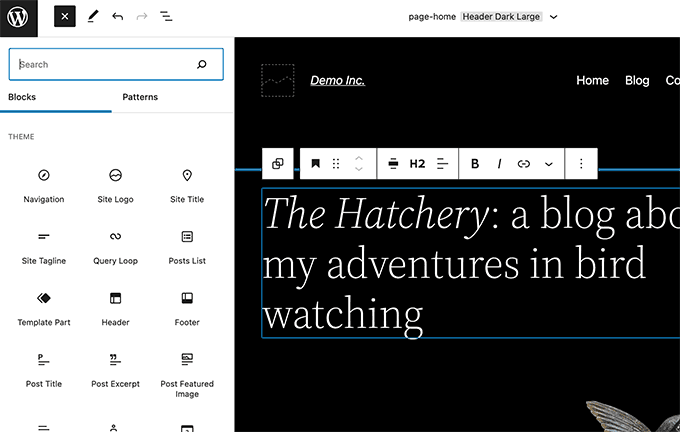
WordPress 6.0 Arturo (2022)
WordPress 6.0 was released in May 2022. It didn’t make any changes to the major components of the user interface, but it made significant upgrades to the site editor experience.
This included adding support for editing more templates and adding more tools to different block settings.
WordPress 6.1 – Misha (2022)
WordPress 6.1 was released in November 2022 and continued with the improvements to the site editor, especially templates and template parts.
This release didn’t make major changes to the core UI itself. However, it added several new tools and enhancements to the block editor. It also started to bring consistency to the block tools and settings.

WordPress 6.2 – Dolphy (2023)
In the first half of 2023, WordPress remained focused on easier site editing and customization.
With the release of WordPress 6.2, the new block-based site editor came out of beta. This allowed users to use the block editor to customize their WordPress themes and create layouts, templates, styles, and more.
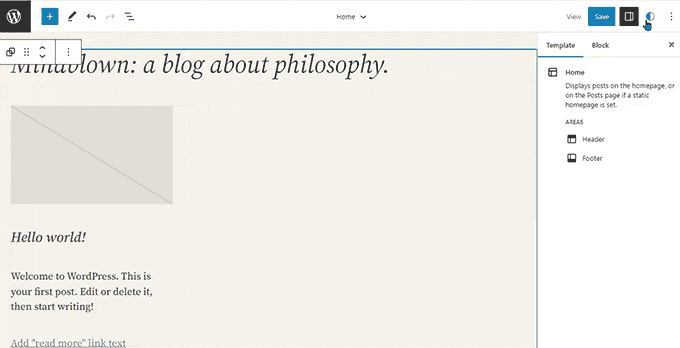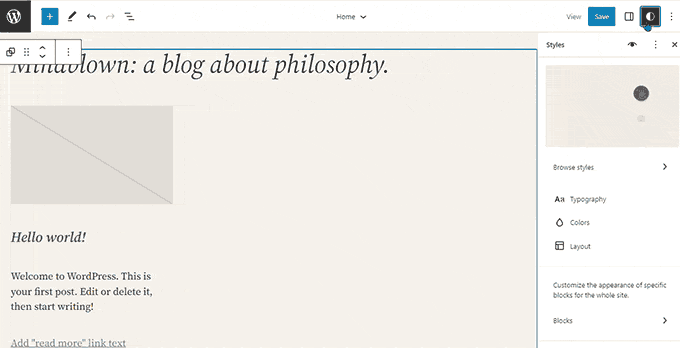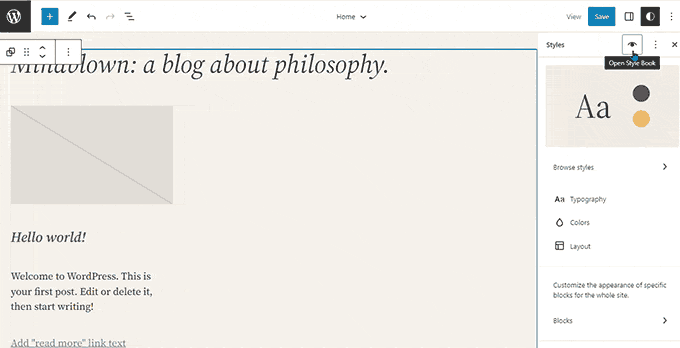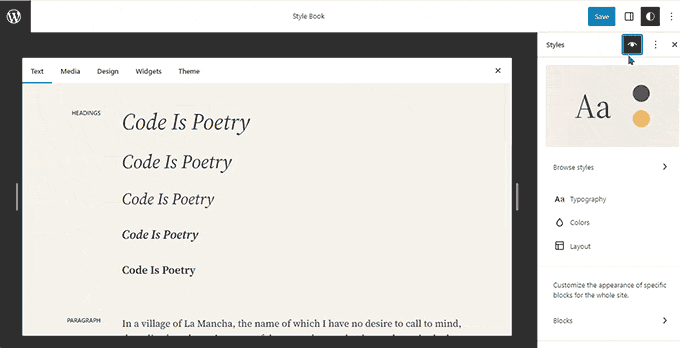
WordPress 6.3 – Lionel (2023)
In the second half of 2023, WordPress released 6.3 with significant updates to the site editor.
It introduced a new navigation screen for the site editor, which provided easier access to templates, pages, patterns, styles, and navigation menus.
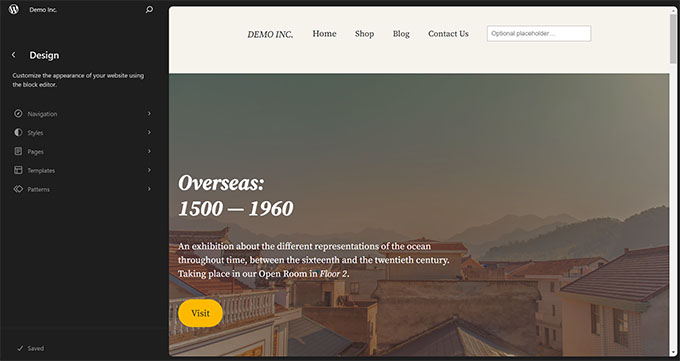
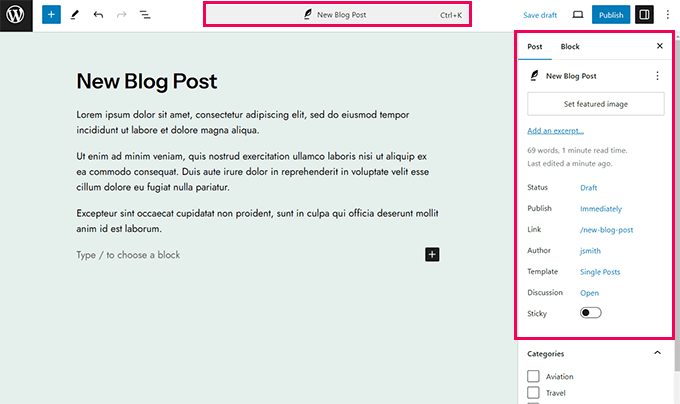
This version also introduced a ‘Command Palette’. Users can launch it with the Command+K or CTRL+K keys on their keyboards.
The command tool also provided easier access to WordPress shortcuts and search for existing content, blocks, patterns, templates, and more.
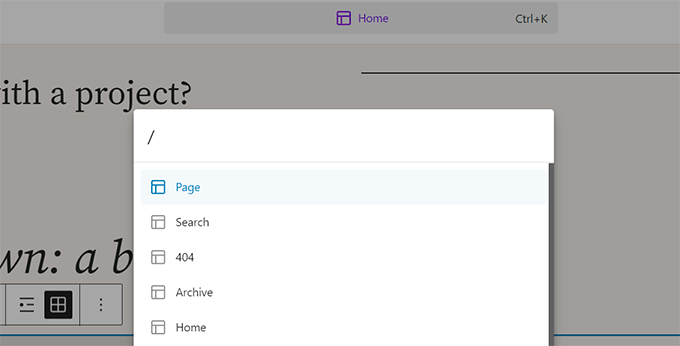
WordPress 6.4 – Shirley (2023)
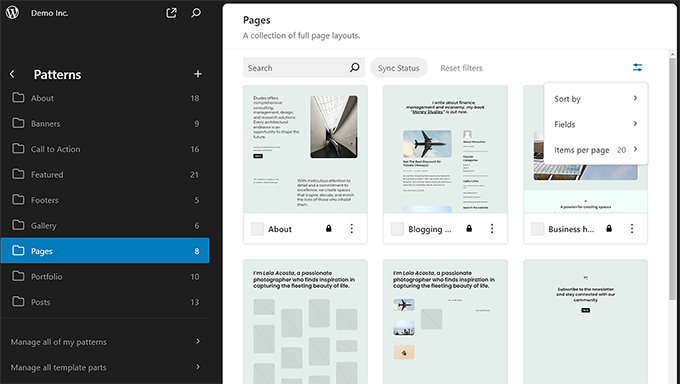
The site editor remained the focus of development for this release. It shipped with a new way to manage patterns and introduced categories to sort patterns easily.
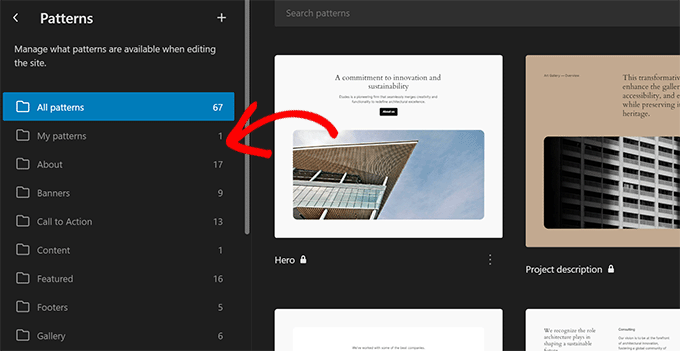
The Command palette introduced new commands and actions to work with blocks. This includes duplicate, transform, delete, or insert commands.
It also got a UI update to make those changes more prominent and usable.
In the upcoming releases, WordPress will be focusing on the site editor, real-time collaboration inside the WordPress editor, and multilingual capabilities.
WordPress 6.5 – Regina (2024)
With the new site editing capabilities, WordPress now has slightly different user interfaces for writing/editing and managing other website tasks, such as installing plugins and themes, moderating comments, and managing settings.
In 2024, WordPress started bringing everything closer by creating consistent workflows for both site and block editor, better data views, and more.
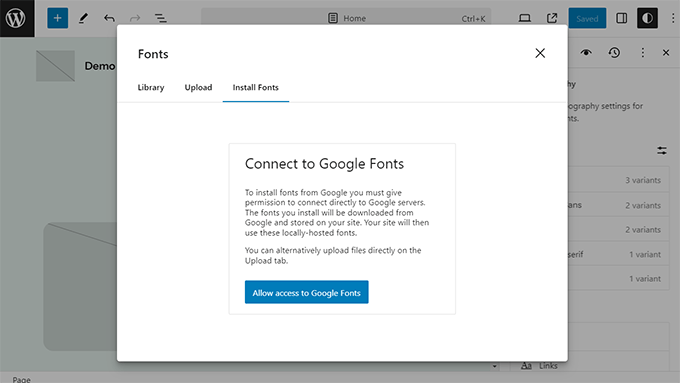
This release also provided a user interface in the site editor for managing and installing fonts using a new feature called Font Library.
Users can see installed fonts, upload custom fonts, and even connect to Google Fonts.
WordPress 6.6 – (2024)
This WordPress release continued to tidy up the user interfaces for the block editor and site editor by making them look consistent.
Slight improvements were made to the block editor so that it looks similar to the site editor’s UI.
There are ongoing efforts to improve and modernize admin design. The changes in the site editor and block editor UI provide some clues as to what direction the new admin design could take.
We hope this article helped you see the evolution of the WordPress user interface since its first release in 2003. You may also want to read the complete history of WordPress or take a look at the top WordPress companies and businesses that grew with WordPress.
If you liked this article, then please subscribe to our YouTube Channel for WordPress video tutorials. You can also find us on Twitter and Facebook.





Syed Balkhi says
Hey WPBeginner readers,
Did you know you can win exciting prizes by commenting on WPBeginner?
Every month, our top blog commenters will win HUGE rewards, including premium WordPress plugin licenses and cash prizes.
You can get more details about the contest from here.
Start sharing your thoughts below to stand a chance to win!
Moinuddin Waheed says
wordpress has travelled this far to become the single largest platform to serve nearly half of all the websites on the internet.
I started using it back in 2016 and it’s been more than 7 years now.
A lot of hardwork in putting and compiling all these memories together with nostalgic thoughts in mind as wpbeginner has also grown along with it.
Thanks wpbeginner for taking us back to the older memories.
Ralph says
Me: I think i started bloggin few years ago
Also me: It is 11 years already?
Jokes aside, this is big nostalgia hit! I used to run a phpbb forums earlier but ditched it for personal website on wordpress. This was great decision as it evloved and upgraded in so many ways!
Ram E. says
And then there’s WordPress 6.4 “Shirley” released this November. My introduction to WordPress occurred in 2013. And I witnessed how the platform has evolved in the last 10 years. It is one of the reasons why I ended up taking a career in marketing. Kudos to the WP Team!
Jiří Vaněk says
Great article, and a big nostalgia trip for me. I started with WordPress in 2007, and since then, it has undergone tremendous development. I remember the times when plugins had to be downloaded and uploaded via FTP, no integrated installation like today. Thank you; it’s a fantastic nostalgia trip looking at those old versions of WordPress.
WPBeginner Support says
Happy to hear we could share some nostalgia
Admin
Michael Sneed says
Lots of hard work compiling all of this… and lots of fun memories!
WPBeginner Support says
Glad we could help bring back your fun memories
Admin
musclegaragefitness says
The evolution of WordPress’s user interface over the years is truly remarkable. It’s fascinating to see how it has transformed from its humble beginnings in 2003 to the user-friendly platform it is today. The dedication of the WordPress team to continually improve the user experience is evident in every iteration. As a long-time WordPress user, I appreciate the effort they’ve put into making it easier for us to create and manage our websites. I can’t wait to see what the future holds for WordPress UI enhancements!
WPBeginner Support says
Glad you’ve enjoyed the evolution of the user interface and we also hope the improvements continue!
Admin
Okan Katan says
Good Informations. Thanks.
eriab nsereko says
we really love you here in africa – just ready for the Kampala WordCamp!
Felipe Elia says
Hey guys! This is an awesome piece of History, congratulations! Can I translate this to Brazilian Portuguese and publish linking to this original? Thanks in advance.
WPBeginner Support says
Hey Felipe
Thanks for the feedback. As for translations, we would appreciate if you quote translated excerpts into your own article, instead of translating the whole article.
Admin
Tegar says
i love wordpress, i like the way you gathered the wp-admin layout
Masud Rana says
Thanks for the gathered history of wordpress.
Trisha says
I’ve just upgraded from 2.7.1 to 2.8.4 and three critical features seem to be missing for me even though others are not having this problem (although some are)
1. Word count on the post write/edit panel is gone;
2. Edit timestamp (to schedule posts) is not working; and
3. Image/media uploader is not working
I’ve already tried disabling all plugins, switching to the default theme, reinstalling WP (not using upgrader), adding a define statement for alternate cron to my wp-config.php, and using multiple browsers/OS – all suggestions from the WP forum, not getting anywhere – hass anyone here heard of these issues and/or know of a fix?
Editorial Staff says
Haven’t had any issues with this. Nor heard of any of the users or client that had this issue. We think that it is the JavaScript that is not working with you. Because there were some issues with TinyMCE that were reported to us. But its user end issue on browsers. You should check to see if you have JavaScript upgraded in your system.
Admin
Trisha says
Thank you for the tip – but I’m a little confused……I was not aware that javascript could be “upgraded”….isn’t it simply a matter of keeping your browser updated? I have the most current versions of both Safari and FIrefox, both of which support the most current version of javascript. Unless you are referring to Java, which I also have the most current version of installed.
And actually quite a few people are complaining in the WP forums about these issues, but none of the suggested solutions work, so I’m trying to reach out beyond the WP forum in the hope that someone else may know of a fix.
I’ll try looking closer at the TinyMCE scripts since you mention that as a possible culprit.
Editorial Staff says
Yes and the problem can also be on your server side. If your server is not updated TinyMCE will have bugs. It happened to a client of ours because they could not move the widgets in the theme page. Please try and see if you are able to do that. If you can’t move things around, it is definitely your host end.
Trisha says
An update in case anyone is interested – after deactivating and reactivating (one by one) all of my plugins the culprit turned out to be the Podpress plugin by MightySeek – i had not upgraded that plugin to it’s latest version because I’d heard that it was not compatible – while the old version worked fine with WP 2.8, it was apparently causing the problems I described – unable to use image uploader or edit timestamp – once I upgraded it now everything is working fine.
plumber randwick says
It looks like They were simple and user interactive style from the beginning,
am using it from 2.6
robby says
world of wordpress reflects the power of community
maybe i should consider to move from blogger to wordpress
Ryan Hamilton says
Wow, got a bit nostalgic there, even though it was only a few years ago. When I was first introduced to 2.0 in 2005 I had no idea it would be nearly as useful and versatile as it now is today.
Here’s to another 4 years.
Scott Bernadot says
This was a great trip thru time. Thanks for putting this all together
Brad says
Great post! That was really cool to see the evolution. Makes me wonder how awesome WP will continue to get…
subcorpus says
just upgraded to baker … the latest version …
lets see how that goes …
Hugo says
Wow… I started using WP in the version 2.5
I have never seen the previous versions… nice post.. thanks
Jason Sack says
I can’t wait for Pepper.
Tom Hermans says
Since WP 2.7 the design of the back-end interface is certainly up to par with the power and possibilities of the WP-CMS. The only thing I don’t like very much is the way the plugins are presented. It used to be easier to see which were active and which were not.. But all in all, that’s a minor issue. Keep up the fantastic work you guys.
grtz,
Tom.
Knoxville Website Design says
It has been a great ride so far ;-).
Giovanni says
WordPress is the primary inspiration for my own CMS
Sebastian Schertel says
Wonderful!
Thank you. I always wanted to see the evolution of the interface. I love wordpress. I wished there would be another wordpress stickers give-away.