If you’re having trouble with the WordPress SEO crawl budget, you’re not alone.
Your crawl budget is basically how often search engines visit and review your site. If it’s too low, your pages might not get indexed quickly, which can hurt your SEO rankings and lower your traffic.
That’s why managing your crawl budget is important if you want to improve your site’s visibility and performance.
At WPBeginner, one of our approaches to managing our crawl budget is keeping our XML sitemaps updated and error-free using the AIOSEO plugin. And when it comes to AIOSEO, there are more features you can use to fix your crawl budget problem.
In this article, we’ll break down the WordPress SEO crawl budget problem and show you simple ways to fix it.

Because this is a huge topic, we’ve broken it down into easy-to-understand sections. Here are the different items we will cover in this article:
Ready? Let’s get started on making sure your pages get the attention they deserve.
How Does Search Crawling Work?
Search engines like Google use sophisticated bots or computer programs to visit websites across the internet. These bots look for changes on your WordPress website and compare them to the main search index.
Let’s say search engines find new content on your site. In this case, they’ll add it to their index. If they find content that’s already in the index but has been updated, they’ll refresh the index with the new information.
Search bots then follow all the links on a page and then repeat the process for those pages.
Now, bots move from one link to another on a page, similar to how real spiders crawl along their webs. That’s why the term crawling is used to describe this activity, and you may sometimes see the bots referred to as search engine spiders.
For better SEO, you’ll need to ensure that search engines can crawl your website easily.
Tip: See our complete WordPress SEO guide for beginners to learn more about SEO.
What Is SEO Crawl Budget?
SEO crawl budget is the number of times search engines like Google will crawl pages on your website.
Google bots crawl billions of pages every day and decide how many pages to crawl on each WordPress site to use their resources wisely. This number isn’t fixed and changes daily based on various factors. So, there’s no set amount of pages the Google bot will crawl on your site or blog.
That said, larger websites with more content generally have a higher crawl budget, and smaller websites have a lower budget.
Other factors also influence the crawl budget, like the popularity of a URL, freshness, update frequency, and more.
Do note that you may lose your crawl budget on unwanted pages for several reasons.
For instance, if your WordPress blog isn’t properly optimized, then search engines will spend your crawl budget on the blog’s less significant parts than important content.
Similarly, you may be accidentally blocking search engines from crawling your website. If this happens, your website may not be using the crawl budget at all.
What Causes WordPress SEO Crawl Budget Issues?
The way WordPress generates URLs and duplicate content can cause crawl budget issues.
For instance, WordPress automatically generates RSS feeds for different areas of your website. There are RSS feeds for:
- The main blog
- Categories and tags
- Comments on each post and page
- Custom post types with separate RSS feed URLs and more.
Links to these RSS feeds are added to your website’s HTML source code, making them discoverable by search engines.
Now, search engines are smart enough to recognize and ignore duplicate content. However, they would still crawl them and spend your SEO crawl budget.
Besides that, search engines would crawl less important items more than needed. This includes archive pages, taxonomies, author archives, and PDF files.
WordPress plugins or other third-party tools can also add query parameters to your WordPress URLs. Google’s spiders may consider these query parameters to be a different page and crawl them.
For instance, UTM parameters are used for Google Analytics tracking, and a page with or without these query parameters would still look the same.
Here’s an example: https://yourdomain.com/landingpage/?utm_source=newsletter
This wastes your SEO crawl budget on less important items and becomes an issue.
How Do You Calculate Your SEO Crawl Budget?
The SEO crawl budget is not a set number of pages. It fluctuates a lot, and there is no reliable way of predicting how many pages Google will crawl on your website on any given day.
However, you can get a pretty decent idea based on recent crawl activity to see how Google crawls your website.
If you haven’t done so, you must first add your website to Google Search Console. It’s a free tool provided by Google to help website owners find out how their website is doing in Google Search.
Simply navigate to your ‘Search Console’ dashboard. Then, you’ll want to switch to the ‘Settings’ menu from the left column and click ‘Open Report’ next to ‘Crawl stats.’
The ‘Crawl’ stats report will show an overview of crawl requests on your website during the last few weeks.
You can hover your mouse over the chart to see how many pages were requested daily.
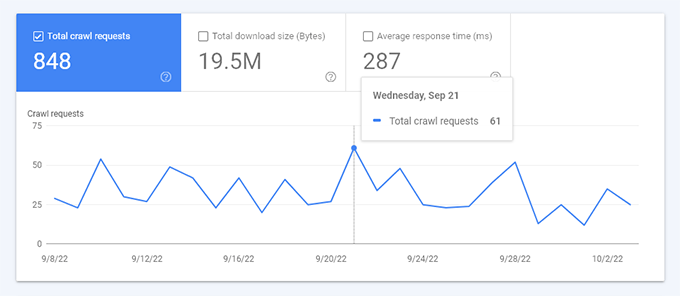
This gives you an idea of the average crawl rate on your site during this period.
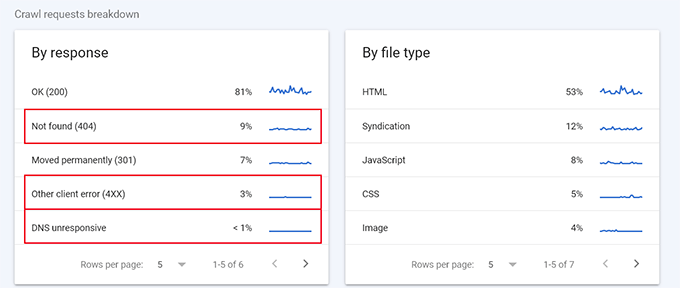
Below, you can see a breakdown of crawl activity by response code, file types, purpose, and Google bot type.
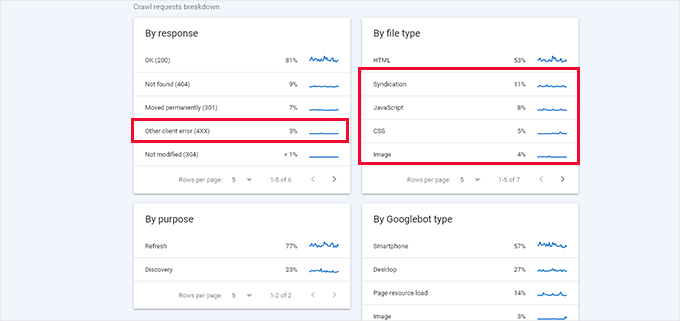
From here, you can see how much the crawl budget is spent on errors, syndication (RSS feeds), JavaScript, CSS, Images, and more.
This gives you a snapshot of items you can optimize to utilize the SEO crawl budget more efficiently. For example, if you have a lot of 404 errors being crawled, you can use a redirection plugin to ensure those crawlers land on helpful content.
(Later in the article, we show you how to redirect crawl errors step-by-step.)
Why You Should Care About SEO Crawl Budget?
Search engines must crawl your website efficiently to index your content on time and properly. However, if your SEO crawl budget is wasted, your important and newer content may not get crawled on time.
It may take weeks for the search engines to notice updates to your older articles or discover new content.
You will miss out on getting traffic from search engines, your SEO rankings may not improve, and you will lose money on sales or ad revenue.
How to Easily Optimize SEO Crawl Budget in WordPress
The easiest and safest way to optimize your SEO crawl budget in WordPress is by using All in One SEO for WordPress, or AIOSEO.
It’s the best WordPress SEO plugin with a built-in SEO crawl optimization tool.
To get started, let’s install and activate the All in One SEO for WordPress plugin first and foremost. If you don’t know how, you can see our step-by-step guide on how to install a WordPress plugin.
Note: There is also a free version of All in One SEO, which also includes a crawl clean-up feature. We recommend using the PRO plan of the paid plugin because it will also give you access to the ‘Redirection Manager’ tool to fix 404 errors on your website.
Upon activation, the plugin will show you a setup wizard. Simply follow the on-screen instructions to set up the plugin.
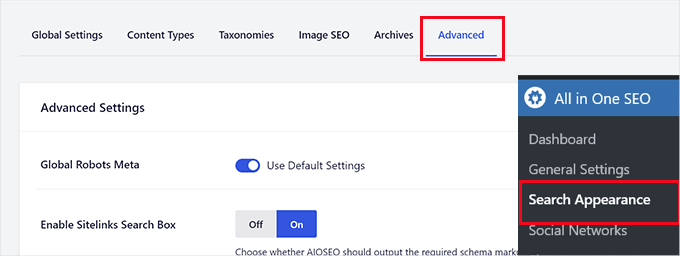
Afterward, you can go to the All in One SEO » Search Appearance section from your WordPress admin area.
Then, you’ll want to switch to the ‘Advanced’ tab.
From here, let’s scroll down to the bottom of the page until you locate the ‘Crawl Cleanup’ option.
Go ahead and click the toggle to enable the ‘Crawl Cleanup’ feature.
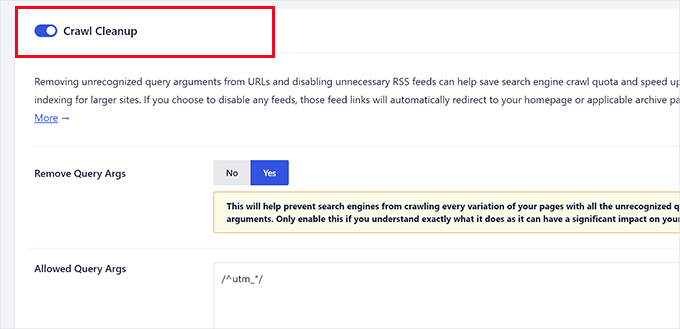
Now, the first option you will see in the crawl cleanup is to remove the query arguments.
Below, you can provide a list of query arguments you want to allow. Advanced users can use Regex regular expressions here.
Next up, you’ll see options for WordPress RSS feeds. All in One SEO will show you all kinds of RSS feeds generated by WordPress, and you can disable the less important RSS feeds.
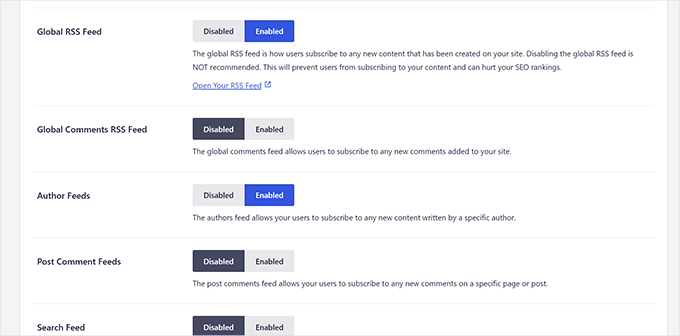
For instance, if you have a single-author blog, you can disable the ‘Author Feeds’ feature.
Once you have disabled all the unwanted RSS feeds, don’t forget to click on the ‘Save Changes’ button to store your settings.
How to Set Up Redirects for Error Pages
All in One SEO will automatically set up redirects for feeds you have disabled. For instance, a tag RSS feed will redirect users to the tag archive page.
You can switch to your Google Search Console dashboard and open the crawl stats report. Here, you’ll see a list of the pages that resulted in errors.
Now, depending on the status code, you can set up redirects for those pages.
For instance, you can redirect 404 errors to a similar page. You can also check other pages with errors and set up redirects for them.
All in One SEO makes setting up redirects on your WordPress website very easy. Simply go to the All in One SEO » Redirects page and add the old URL under the ‘Source URL’ and the new URL under the ‘Target URL’ field.
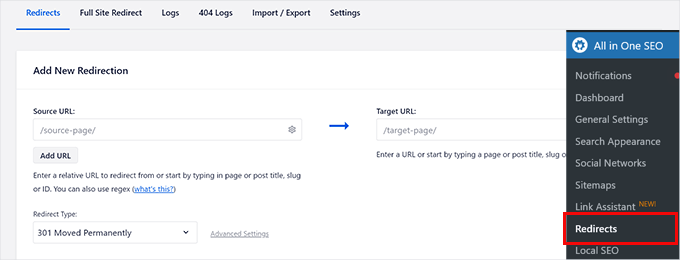
Go ahead and click on the ‘Add Redirect’ button to save your settings.
Then, you can just repeat the process to set up more redirects as needed. For more details and alternate methods, see our guide on how to set up redirects in WordPress.
Bonus Tip: Creating a Sitemap in WordPress
An XML sitemap is a special file that lists all the pages on your website in a format search engines like Google can easily read. Think of it as a map for search engines to find and index your content.
Having an XML sitemap doesn’t directly boost your search rankings, but it helps search engines find and index more of your content.
This is especially useful for new websites or blogs without many backlinks, as it helps search engines discover all your pages. Even for established sites, sitemaps highlight important pages and update frequency, making it easier for search engines to index your content effectively.
For more on this topic, you can check out our guide on what is an XML sitemap and how to create one in WordPress.
We hope this article helped you learn about the WordPress SEO crawl budget problem and how to fix it. You may also want to see these expert tips on using Google Search Console to grow traffic or see practical examples of how to improve the organic click-through rate in WordPress.
If you liked this article, then please subscribe to our YouTube Channel for WordPress video tutorials. You can also find us on Twitter and Facebook.




Mrteesurez
This is really new to me as I didn’t know what’s called SEO crawl budget. After reading this guide I now realized the reasons some of the changes I made sometime take time to reflect on Google search. Every bloggers need to know this, learn it and know how to best use his SEO crawl budget.
This is an educative article, I have learnt new concept here, thanks
Jiří Vaněk
I have a custom 404 page set up and here, in addition to apologizing to readers, I also have links to interesting content on the site that might interest them. Can this option also help?
WPBeginner Support
A 404 page would not affect you SEO crawl budget.
Admin
Jiří Vaněk
Thank you for answer. I didn’t know that, so again I know something new thanks to you.
Moinuddin Waheed
This is completely new concept to and I have come to know about crawl budget and its importance.
since crawl budget is given by Google itself and index web pages on its basis, what is the criteria for large and small websites and what are factors contributing to crawl budget?
WPBeginner Support
For the moment that is not publicly shared information which is why we recommend taking a look at the Crawl report to get an idea of what you have for your site.
Admin
ASHIKUR RAHMAN
how can i tell google to not crawl /feed/ links? most of our post is indexed. but same or more number of postlinks/feed/ is crawling by google. in gsc these links becomes duplicate link.
WPBeginner Support
You would want to noindex your feed to prevent Google from crawling it, if you have a SEO plugin on your site, those would normally have settings to quickly noindex your feed.
Admin