In my early freelancing days, I once made a code change that broke a client’s site. Thankfully, I had a backup so I quickly restored the website but I lost the changes I had already made.
That’s when I started using Git. It is a version control system that allows you to easily save all your changes and roll back at any time.
Whether you’re working alone or with a team, Git tracks every update, big or small. This keeps your projects organized and makes collaboration much smoother.
In this guide, I’ll walk you through exactly how I use Git for WordPress development. I’ll show you, step-by-step, how to set it up and manage your themes and plugins like a pro.
TL;DR: The Short Version
What is Git? It’s a version control system that acts like a “save” button for your code, letting you track every change.
Why use it with WordPress? It helps you develop themes and plugins safely, collaborate with others, and easily undo mistakes.
What will you learn? This guide shows you how to install Git, connect it to a cloud service called GitHub, and deploy your work to a live website.

Here’s an overview of everything I will cover in this guide. You can click the links below to jump ahead to any section:
- What Is Git?
- Git vs. GitHub – What's the Difference?
- How to Use Git and GitHub for WordPress Development
- Setting Up a Local WordPress Environment for Git
- Installing Git Locally and Creating a Repository
- Pushing Your Local Project to a New GitHub Repository
- Deploy GitHub Themes and Plugins to a Live WordPress Site
- Install WordPress Plugins and Themes from GitHub
- Important Git and GitHub Terms You Should Know
- Bonus Resources
- Frequently Asked Questions About Using Git with WordPress
What Is Git?
Git is a free, open-source version control system designed to handle everything from small to very large projects with speed and efficiency. It helps you keep track of changes made to your code or files over time.
Everything is stored inside a folder called a repository, or repo for short. Think of it as a master folder where Git monitors all your project files.
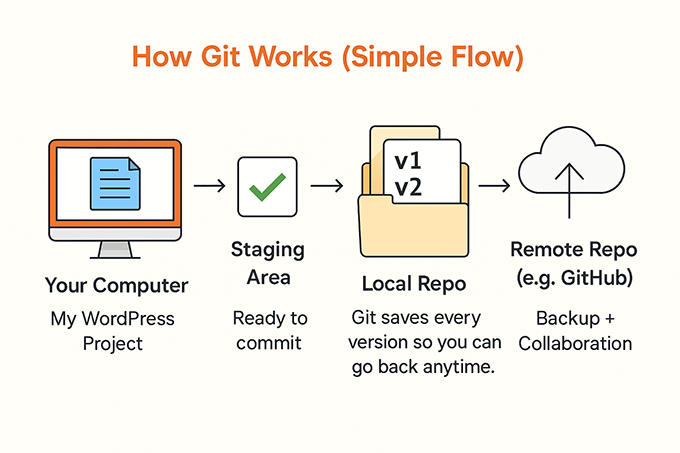
Git is mostly used by developers working on different software development projects. It lets multiple people copy the main codebase to their computers.
Each person can make changes locally without touching the original files. Once they’re done, they can submit their updates to a platform like GitHub, which helps manage and organize team contributions.
Git vs. GitHub – What’s the Difference?
A common point of confusion is the difference between Git and GitHub. If you’re just starting out, it’s easy to mix them up. Here’s a simple breakdown:
| Git | GitHub |
|---|---|
| The Tool | The Service |
| Installed and run locally on your computer. | A cloud-based platform that hosts Git repositories. |
| Core function is version control and tracking changes. | Core function is collaboration and sharing repositories. |
| You can use Git without GitHub. | GitHub doesn’t work without Git. |
There are other Git hosting services too, like Bitbucket, Launchpad, and Assembla. But GitHub is the most popular, thanks to its extra features and clean interface.
It’s especially helpful for teams and remote workers managing large projects. You can track every change, leave comments, and roll back to earlier versions when needed.
And because everything is stored in the cloud, you won’t lose your work if your computer crashes or gets lost.
Next, we’ll look at when it makes sense to use Git and GitHub for WordPress development.
How to Use Git and GitHub for WordPress Development
At WPBeginner and our partner companies we mostly use Git and GitHub when building custom WordPress plugins and websites. They are perfect tools for keeping everything tidy while working through different versions and updates. Here are the primary use cases:
- Developing custom WordPress themes and plugins: GitHub can hold the entire codebase. You can clone the repo, make changes, and test on a local site before pushing to the live version.
- Collaborating with a team of developers: Git allows multiple people to work on the same project without overwriting each other’s code.
- Managing code changes and rolling back safely: Git’s version control means you can revert to any previous version of your code if a bug is introduced.
- Contributing to open-source WordPress projects: Many WordPress plugins and themes on GitHub are open-source. Anyone can “fork” the repo, work on bug fixes or new features, and submit their contributions with a pull request.
You can even use GitHub to download WordPress plugins or themes and install them manually. Just keep in mind that GitHub isn’t built to work like cloud storage tools such as Dropbox or Google Drive.
Next, we’ll show you how to make a change to a local plugin file and upload it to GitHub step by step.
Setting Up a Local WordPress Environment for Git
Before using Git and GitHub, it’s a best practice to create a local WordPress environment. This is where you can work on your project, make changes to a WordPress site, try your new code, and test plugin and theme development.
Having a local environment ensures that your live website is not affected by the changes until you deploy them. In case anything goes wrong, you can make changes and debug the code on your local website.
To get started, you can use local web software that lets you host local sites on your computer instead of a staging or live server.
For example, software like Local WP (previously known as Local by Flywheel), MAMP, XAMPP, and WampServer are great for creating local environments. They’re free to use and very easy to set up.
You can learn more by following our guides on how to install WordPress on a Windows computer and how to install WordPress locally on a Mac.
Before we start installing Git, it’s important to know what command line is. This is a text-based interface for your computer. Don’t worry, it’s not as scary as it looks! On Mac or Linux, it’s called Terminal. On Windows, it can be Command Prompt or a special tool we’ll install called Git Bash.
Installing Git Locally and Creating a Repository
Step 1. Check if Git is already installed
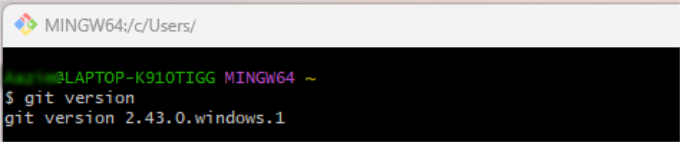
Once your local environment is ready, the first step is to check if Git is already on your machine. Many newer computers, especially macOS and Linux devices, have it pre-installed. To check, open Terminal (Mac/Linux) or Command Prompt (Windows) and type the following command, then press Enter:
git --version
If Git is installed, you will see its version number. If you get an “unknown command” error, it means you need to install it.
Step 2. Download and Install Git
Visit the official Git website and go to the ‘Downloads’ section.
Click the link for your operating system to download the installer. After it downloads, run the installation wizard and follow the on-screen instructions, accepting the default settings.
Step 3. Create a Local Git Repository
Now that Git is installed, you need to tell it which folder to start tracking. First, navigate to your local WordPress site’s files. Find the wp-content folder and go into the specific plugin or theme folder you are working on. Next, you need to open your command-line tool inside this folder.
- For all systems (universal method): Open your command line tool (Terminal, Command Prompt, etc.). Type
cdfollowed by a space, then drag and drop your project folder into the window. This will paste the folder’s path. Hit Enter to navigate there. - For Windows users (shortcut): If you chose the option during installation, you can simply right-click anywhere inside your project folder and select ‘Open Git Bash Here’.
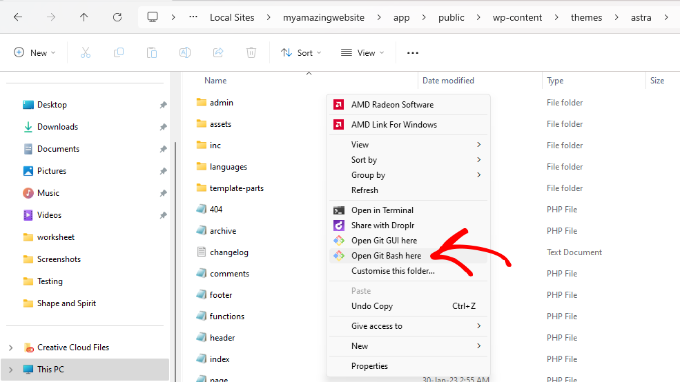
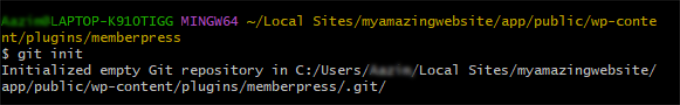
Once your command line is open in the correct folder, type the following command and press Enter. This initializes or creates a new, empty repository.
git init
Step 4. Stage Your Files for Committing
Now you need to tell Git which files you want to include in your first “snapshot” or save point. You can think of this as putting all your files into a shopping cart before you check out. The following command adds all files in the current folder to the “staging area.”
git add .
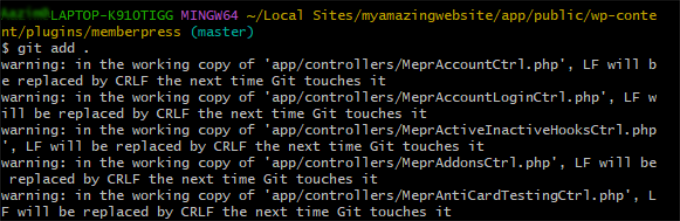
Step 5. Commit Your Changes
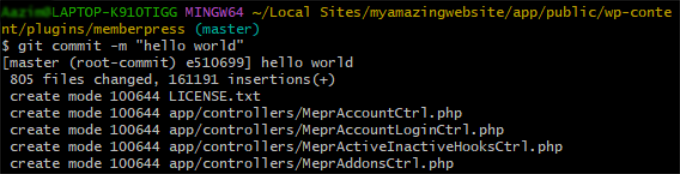
A “commit” finalizes the changes you’ve staged. It’s like going to the checkout, paying, and getting a receipt for your purchase. This command saves your staged files as a new version in the repository’s history, along with a descriptive message.
git commit -m “First commit”
You can replace “First commit” with any message that describes the changes you made. This is very helpful for keeping a record of your work.
After running these commands, you’ll see a hidden ‘.git’ folder in your project directory. This is where Git stores all its tracking information.
Pushing Your Local Project to a New GitHub Repository
Step 1. Sign Up for a Free GitHub Account
First, head to the GitHub website and sign up for a free account. You’ll just need to enter your email and follow the on-screen instructions.
Step 2. Create a New Repository
Once you’re logged into your GitHub dashboard, click the ‘+’ sign in the top right corner and select ‘New repository’.
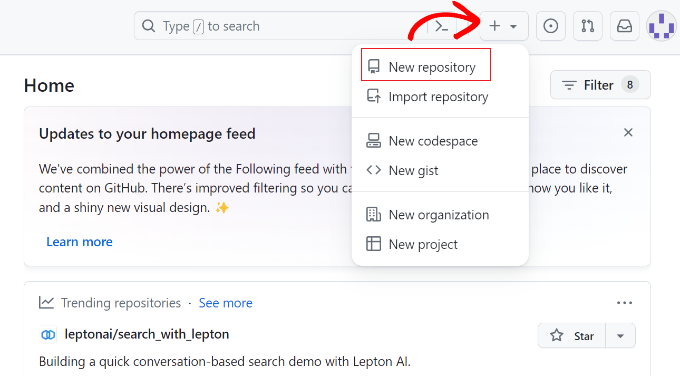
On the next screen, give your repository a name. You can also add a description and choose to make it public or private. When you’re done, click the ‘Create repository’ button.
Step 3. Copy the Repository URL
After creating the repository, you’ll be taken to a setup page. Copy the URL provided under the “Quick setup” section.
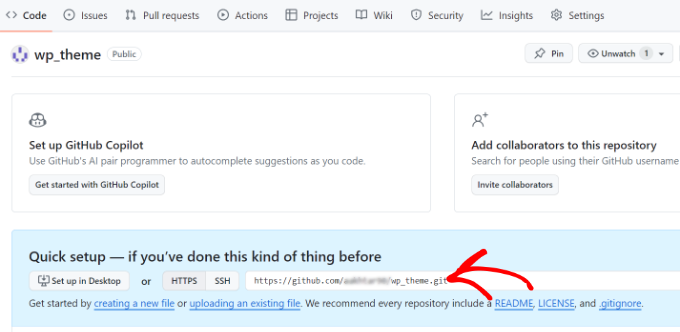
Step 4. Link Your Local Repository to GitHub
Go back to your command-line tool (Git Bash, Terminal). Type the following command, but replace ‘URL’ with the repository link you just copied. This command tells your local Git project where its remote counterpart lives on GitHub.
git remote add origin URL

Step 5. Push Your Local Files to GitHub
Finally, use the following command to “push” or upload all the commits from your local machine to the remote repository on GitHub.
git push -u origin main
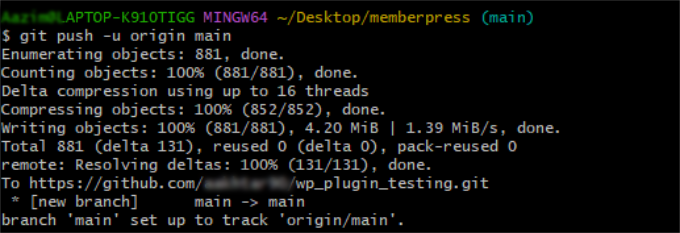
The first time you do this, you may be asked to sign in to your GitHub account to authorize the connection. Once it’s complete, you can refresh your repository page on GitHub and see all your local files.
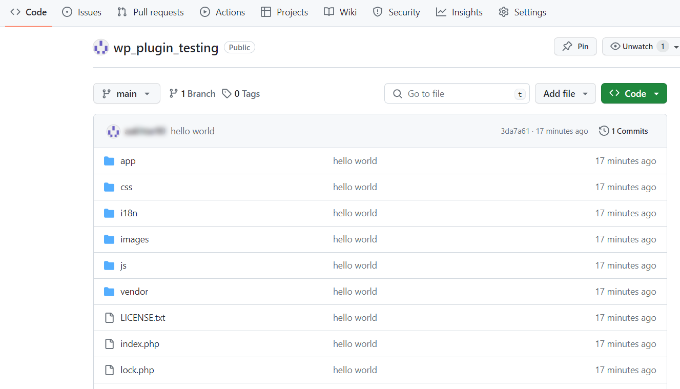
How to Pull Updates from GitHub to Your Local Machine
If you or a teammate makes changes directly on GitHub, you’ll need to update your local files to match. The ‘pull’ command downloads all changes from the remote repository and merges them into your local project. This ensures you’re always working with the latest version.
To do this, open your command-line tool in your project folder and type the following command:
git pull origin main
Once you’ve made the changes to the local files, the next step is to push them to the live site.
Deploy GitHub Themes and Plugins to a Live WordPress Site
After you’ve finished developing your WordPress plugin or theme, the last step is to deploy it on your live website. While you can do this manually with Git commands, a WordPress plugin like WP Pusher makes the process much easier.
- Visit the WP Pusher website and download the plugin ZIP file to your computer.
- In your live WordPress site’s dashboard, install and activate the WP Pusher plugin. If you need help, see our guide on how to install a WordPress plugin.
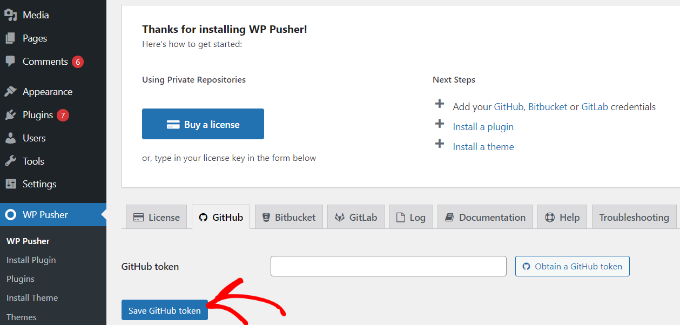
- Upon activation, navigate to WP Pusher from your WordPress dashboard and click the ‘GitHub’ tab. From there, click the ‘Obtain a GitHub token’ button.
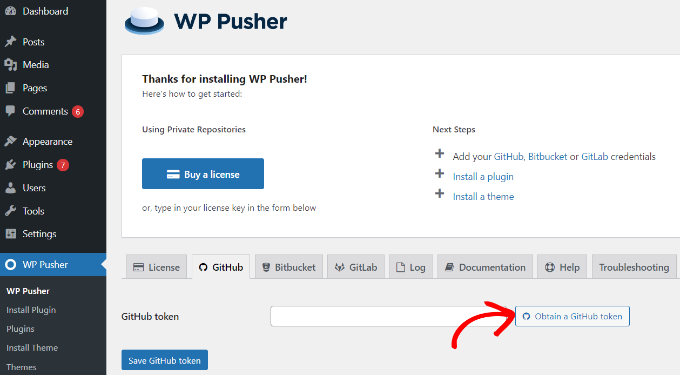
- A new window will open asking you to authorize the connection to your GitHub account. Click the ‘Authorize wppusher’ button.
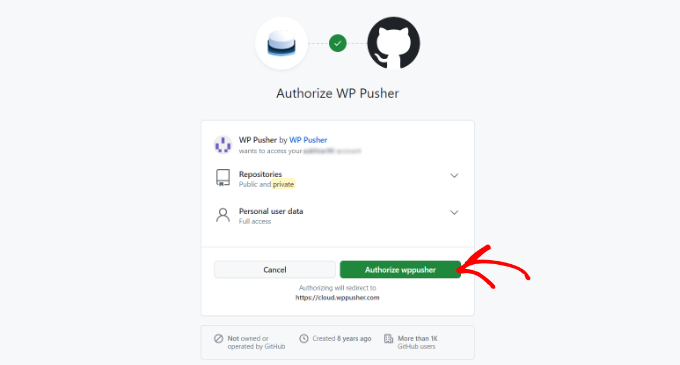
- After authorizing, GitHub will show you a token code. Copy this code.
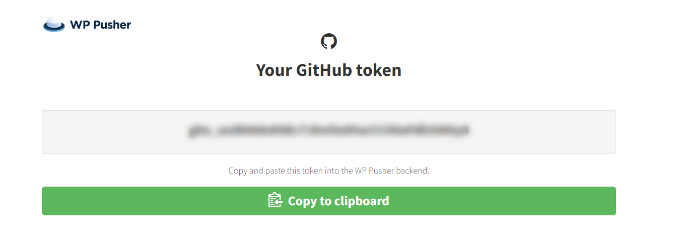
- Go back to your WordPress dashboard, paste the token into the field, and click ‘Save GitHub Token’.
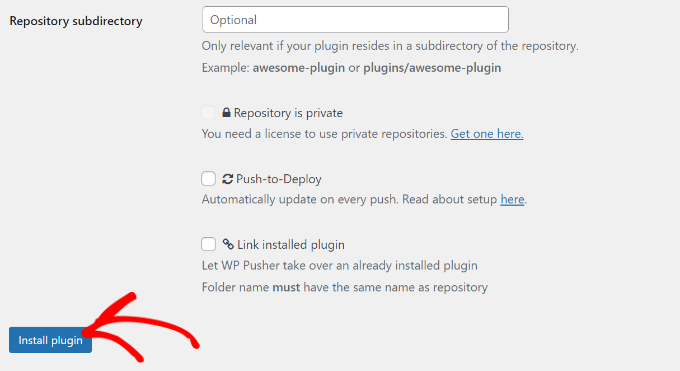
- Now you can install your project. Go to WP Pusher » Install Plugin (or Install Theme). You can click ‘Pick from GitHub’ to find your repository or paste its URL directly. Finally, click the ‘Install plugin’ button.
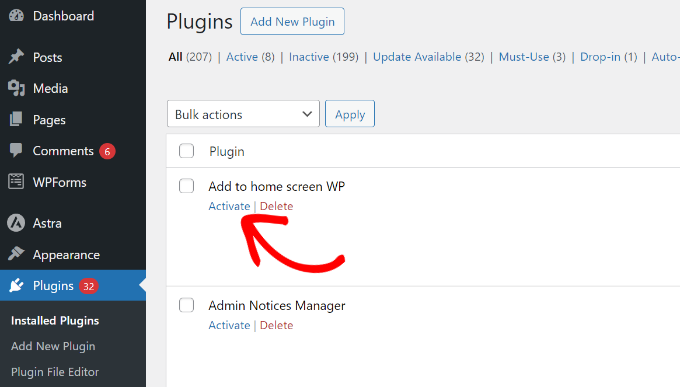
- Once installed, go to Plugins » Installed Plugins and click the ‘Activate’ link under your new plugin to start using it.
Install WordPress Plugins and Themes from GitHub
You can also download plugins and themes directly from GitHub, which is useful if they are not available in the official WordPress.org directory. Many WordPress developers host their projects there.
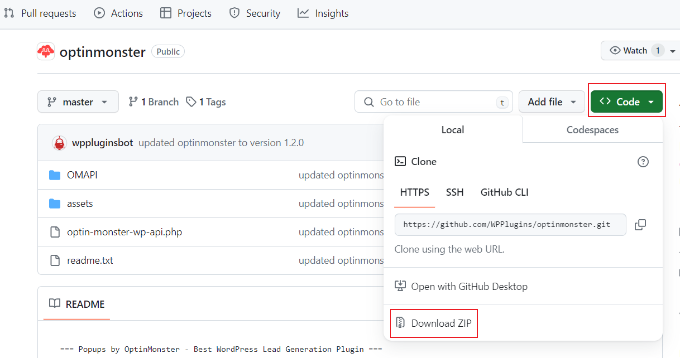
- Navigate to the plugin or theme repository you want to install on GitHub.
- Click the green ‘Code’ button and select the ‘Download ZIP’ option to save the files to your computer.
- In your WordPress dashboard, go to Plugins » Add New » Upload Plugin (or Appearance » Themes » Add New » Upload Theme) and upload the ZIP file you just downloaded.
For more details, please see our guide on how to install WordPress plugins and themes from GitHub.
Important Git and GitHub Terms You Should Know
You’ll come across different Git and GitHub terminologies as you start to use them for WordPress development and other purposes. To help you out, here are some important terms you should know:
- Branches – A branch is like a parallel repository that you can create. It lets you make changes and work freely without affecting the main branch or disrupting the live version.
- Merge – When you want to take changes from one branch and apply them to another branch, then this process is called merging. However, the branches need to be in the same repository or from a fork.
- Pull – It refers to fetching changes and merging them. Let’s say someone made changes to a file in the repository. You can pull those changes to your local environment to ensure your files are up to date.
- Pull Requests (PR) – A pull request is when a user submits proposed changes to a repository, and it is accepted or rejected by another repository collaborator.
- Fork – A fork is a personal copy of another user’s repository that you have on your account. You can make changes to a project freely using a fork without affecting the original repository.
- Commit – A commit is an individual change to a file in the repository. When you make a commit, Git will create a unique ID to help you keep a record of specific changes. It also records who made the changes and when they were made.
- Push – Pushing means sending your changes to a remote repository on GitHub. For instance, if you make changes to a file locally, then you can push them so others can also access them.
Bonus Resources
At WPBeginner, we love it when our beginner readers graduate to the advanced level and want to write code themselves. If you are interested in WordPress coding and development, then here are a few resources that you will find helpful.
- Useful WordPress Code Snippets for Beginners (Expert Pick)
- How to Automatically Deploy WordPress Theme Changes Using GitHub and Deploy
- Best WordPress Development Tools (Free + Paid)
- How to Add Dummy Content for Theme Development in WordPress
- 19 Best WordPress Starter Themes for Developers
Frequently Asked Questions About Using Git with WordPress
Following are answers to some of the most commonly asked questions I have come across.
Is Git difficult to learn for beginners?
Like any new tool, Git has a learning curve. However, you only need to learn a few basic commands to get started, which we’ve covered in this guide. Once you understand the core concepts of committing, pushing, and pulling, it becomes much easier.
Can I use Git for a live WordPress site without a local environment?
While technically possible, it is strongly discouraged. Making changes directly on a live site is risky. A local environment gives you a safe sandbox to test your code thoroughly before deploying it, which is the whole point of using a version control system like Git.
What is the main advantage of using GitHub with Git?
The main advantage is collaboration and backup. Git by itself tracks versions on your local machine. GitHub provides a centralized, cloud-based location to store your code, share it with team members, review changes, and ensure your project is safe even if your computer fails.
Is GitHub for coding only?
No, not at all! While its primary use is for software development, GitHub’s version control is useful for any project where you need to track changes over time. People use it for writing books, managing academic research, collaborating on legal documents, and even tracking changes to design files.
What is GitHub Copilot?
GitHub Copilot is an AI-powered tool that acts like a pair programmer. As you write code, it suggests entire lines or even complete functions in real-time. It helps developers write code faster, learn new languages, and reduce the time spent searching for solutions.
I hope this article helped you learn how to use Git with WordPress. You may also want to see our picks of the best mobile apps to manage your WordPress site and the most common WordPress errors and how to fix them.
If you liked this article, then please subscribe to our YouTube Channel for WordPress video tutorials. You can also find us on Twitter and Facebook.




Oyatogun Oluwaseun Samuel
Git and GitHub are really great tools that makes the life of developers easier if one can learn it. I always tells everyone even beginner to consider it. It really is a great tool. Thanks for sharing this.
Prajwal Shewatkar
Git is the best alternative to manual backups every time you make changes to a code. I’ve used it while working on a simple sort and list plugin that I built for my client project. It saves a lot of time and it’s very easy to roll back when you mess things up.!
Mrteesurez
Thanks for this idea. although I have learnt some basic things about Git in this guide but I still need to learn it very well. It will be good to be using for Backup so that I can save time from doing backup whenever I make small changes.
Jiří Vaněk
Hi Mr. Mrteesurez . For beginners, it’s better to use something like Duplicator and set up automatic and regular backups. GitHub, in my opinion, is more intended for development. When you’re debugging some code, creating a plugin, etc., you can save versions, and the great thing is that you can work on it as a team. GitHub is still complicated for me, but I’m starting to learn it as well. However, if you’re specifically looking for backups, try Duplicator. It’s a great plugin, even from the wpbeginner team, and automatic backups to Google Drive are flawless.
Jiří Vaněk
I have been interested in Github and versioning for a long time. Great article as a start to finally learn GitHub. Thank you for your work. Thank you also for the basic commands.