WYSIWYG is an acronym for What You See Is What You Get. It is used for tools where you create/edit content in real time and see a live preview as you work.
These editors are incredibly useful online, especially when creating content for websites. Whether you are writing a blog post, crafting an email, or designing a webpage, a WYSIWYG editor makes the job easier and more efficient.

Why Use WYSIWYG Editor?
WYSIWYG editors come with many features that enhance your content creation process. The functionality and look are generally the same whether you have a WordPress website or use a different content management system (CMS).

For the most part, you will find that they all have the following features:
- Text Formatting: These editors allow you to bold, italic, underline, and strikethrough your text just like you would in a word processor. In fact, these are often called rich text editors because they allow you to edit content in a familiar way, just like in Microsoft Word.
- Links: You can easily add links to your content by simply clicking a button in a toolbar and pasting the URL. You won’t have to add or edit HTML code to create your content.
- Images: Adding images is a breeze. You can upload them directly from your device or insert them from an online source. Many WYSIWYG editors will even let you paste an image directly inline.
- Table Creation: Need to present data neatly? WYSIWYG editors enable you to create tables within your content without dealing with other web applications, such as Google Sheets, or needing special embeds.
But that’s not all. WYSIWYG editors also offer features like spell check, source code view, and more. All these features make it easier for you to focus on creating quality content without worrying about learning PHP, CSS, or web design.
Additional Functionality of WYSIWYG Editors
In addition to the above, WYSIWYG editors tend to have a bunch of features designed to simplify and enhance your content creation process.
Most WYSIWYG editors have built-in spellcheck. This built-in tool is quite handy, automatically underlining incorrectly spelled words, helping you avoid any embarrassing typos in your content.
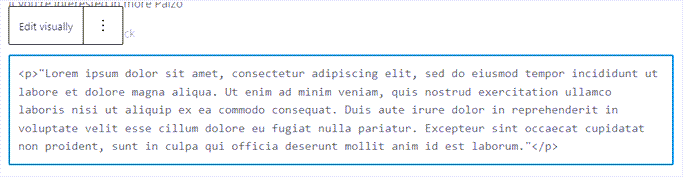
Another extremely vital part of WYSIWYG is the HTML code view. This lets you switch between the visual design and markup views seamlessly.
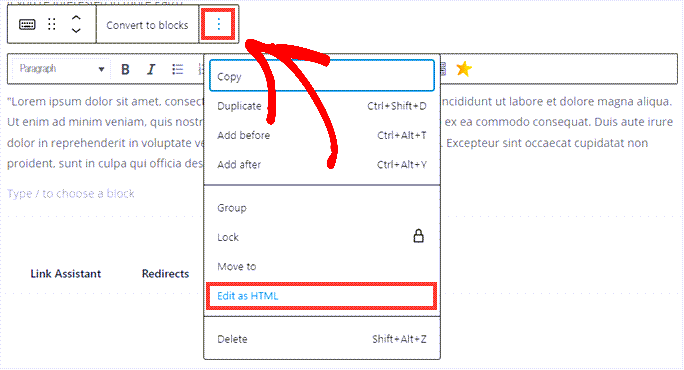
Looking at the HTML code is perfect for when you need to troubleshoot things.
These might be things like issues with images or incorrect text formatting due to copy/paste.
Not to mention, many WYSIWYG editors come with a robust set of design tools. For instance, the Gutenberg editor for WordPress is an interactive, drag-and-drop design tool that lets you write content and use templates to create whatever you can imagine right in front of your eyes.
The interface is always user-friendly, so even if you’re not a tech whiz, you’ll be able to make your content look professional and polished with just a few clicks.
WordPress Block Editor
The Gutenberg Editor was introduced in 2018 and has changed the user interface for creating content with WordPress.
At its core, Gutenberg is a block-based editor that you can use on either the frontend or backend of your site.
Instead of writing and designing in one large text area, as in a rich text editor like TinyMCE, you create your content using individual blocks. TinyMCE is an open source WYSIWYG editor used as the base for the previous WordPress content editor, now called the classic editor.
These can be anything from paragraphs and headings to images, videos, quotes, or even more complex elements like tables or custom HTML markup.
Each Gutenberg block can be individually customized and moved around, granting you unprecedented control over your content’s layout and design. You can even use pre-made designs called Patterns to have a template to work with right inside the block editor.

You can move blocks around in real time and see exactly what your blog post or landing page will look like before you ever publish.
Gutenberg isn’t the only WYSIWYG editor for web design, though. Non-WordPress website builders like Squarespace offer WYSIWYG editing, and other WordPress themes and plugins like SeedProd and Divi do, too.
SeedProd’s WSYIWYG interface is simple and intuitive, whether you are editing text or your entire layout.

Many of these tools have more advanced functionality and better user experience than Gutenberg, so lots of pro users begin using them as they continue improving their web development skills.
Common Issues in WYSIWYG Editing
As you start to use WYSIWYG editors more frequently, it’s inevitable that you will encounter some issues or obstacles. But don’t worry! Most of these common problems have straightforward solutions. Let’s take a look at some of them.
Formatting Issues
One common issue you might encounter is formatting. For example, your text may not align correctly, or the font size might not adjust as you want. This is often due to copied text bringing in additional HTML, CSS, or even JavaScript.
To fix this, try pasting your text into a plain text editor first, like Notepad++. Then, copy it from there into the WYSIWYG editor. This usually strips out any additional code, allowing the WYSIWYG editor to better format the text.
Doing this will also strip links and images, so you will need to reinsert them using the rich text editor or HTML code view.
Images Not Displaying
Another common issue is that images do not display properly or at all. This could be because the image URL is incorrect or the image file is not supported. Always double-check that your URL is correct. If you are uploading images, make sure they are in a web-friendly format, such as .jpg, .png, or .gif.
For example, if you use a format like .svg, WordPress needs an extra tweak to work right. For more information, you can check out our guide on how to get SVG files to work safely with WordPress.
Unexpected Code Changes
Sometimes, you might find that the code changes unexpectedly after saving. WYSIWYG editors are not perfect and can add additional HTML or CSS that you didn’t intend. This can change the look and feel of your content.
To remedy this, you could switch to the HTML code view and manually remove any unwanted code. Be careful, though, as you need a basic understanding of HTML markup to do this safely.
Browser Compatibility Issues
Finally, you may encounter issues when viewing your content on different browsers. Not all browsers interpret HTML and CSS in the same way, and JavaScript can act differently depending on your system settings.
This can all lead to inconsistencies in how your content is displayed. Always test your site in multiple browsers, including Chrome, Firefox, Safari, and Microsoft Edge, to be sure that your content looks good no matter where it’s viewed.
Final Thoughts on WYSIWYG Editors
WYSIWYG editors, like the WordPress Gutenberg Block Editor or even the older, open-source TinyMCE classic editor, are vital tools that can significantly simplify your content creation process.
With features like drag-and-drop real-time editing, HTML code view, and templates, these web design tools allow you to focus more on your content’s quality rather than coding.
We hope this has taught you about WYSIWYG editors and how they can help you improve your web design skills. You can also check out our expert picks of the best drag and drop page builders for WordPress and our guide on how to choose the best web design software for your site.
Additional Resources
- Text Editor
- Best WordPress Landing Page Plugins Compared
- Shortcodes
- Page Builder
- Default Theme
- Most Common WordPress Errors and How to Fix Them
- How to Properly Switch From Wix to WordPress (Step by Step)
If you liked this article, then please subscribe to our YouTube Channel for WordPress video tutorials. You can also find us on Twitter and Facebook.