In WordPress, a user role defines what a logged-in user can do on your WordPress website. Some users may have full control over your site, while others may only be able to do certain tasks, like creating posts, editing content, or moderating comments.
To see the default WordPress user roles, you can go to the Users page in the WordPress dashboard. There are 5 default user roles: Administrator, Editor, Author, Contributor, and Subscriber.
You can think of WordPress user roles like the levels of access people have at a school:
- The principal and maintenance worker can go anywhere in the school they need to.
- Teachers will have access to their own classrooms, but not other classrooms or the principal’s office.
- Visiting parents may not be allowed to go beyond the lobby.
What Is a User in WordPress?
In WordPress, a user is someone who is registered on your WordPress website so that they can log in with a username and password. Someone who’s just viewing your site doesn’t have to be a registered user.
As the owner of your WordPress site, you are a registered user. You can also add other people as users with their own login credentials.
You might want to give people access to log in to your site so they can:
- Write a guest post on your blog.
- Help you with troubleshooting WordPress errors.
- Get access to exclusive content on your membership site.
But what if you want to limit their access, like in our school analogy? You wouldn’t want to let parents into the principal’s office where they could change their child’s grades, for example.
It’s the same idea for your WordPress site. Giving people access to everything on your site can be risky. As a site owner, you need to know how to keep your WordPress website secure.
Luckily, WordPress has a built-in way to control what your users can access, with user roles.
What Are the Default User Role Categories in WordPress?
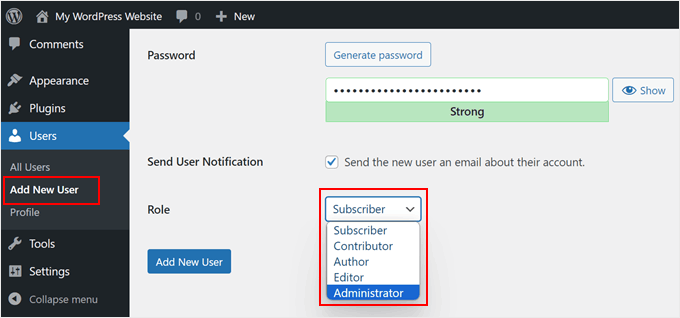
If you open your WordPress dashboard and go to Users » Add New User, you will see a list of the default WordPress user roles in the ‘Role’ dropdown menu.
These are Administrator, Editor, Author, Contributor, and Subscriber.
You can see a full visual comparison between each user role on our user roles infographic, and you’ll find more detailed information in our beginner’s guide on WordPress user roles and user permissions.
Read on for a brief summary of the different user roles in WordPress.

1. Administrator Role
On a regular WordPress website, a site administrator has the most powerful role and complete control over the WordPress backend. They can add new posts, and edit or delete posts by any user. Plus, they can install, edit, and delete plugins, themes, and widgets.
When you first create a WordPress website, you are automatically given the user role of administrator. As an admin, you get to decide who gets access to your WordPress website and define what they can and cannot do.
Most importantly, admin users can create users, remove them, and change information about existing users, including their passwords.
However, WordPress multisite networks have an even more powerful role: the super admin role. Super administrators have admin access to every single site in the multisite installation.
2. Editor Role
In WordPress, editors have full control of the content sections of your website. They can add, edit, publish, and delete posts, and can moderate, edit, and delete comments as well.
However, editors do not have access to change your site settings, install plugins and themes, or add new users.
3. Author Role
Authors can write, edit, and publish their own posts, but can’t modify posts by other users. They can also delete their own posts, even if they are already published.
While they can view comments, authors can’t moderate, approve, or delete them. They also don’t have access to site settings, plugins, or themes.
4. Contributor Role
Users with the contributor role can add new posts and edit posts, but can’t publish any posts. They also can’t upload files, which means they can’t add images to their posts.
They don’t have access to website settings, plugins, or themes, so they cannot change any settings on your site.
5. Subscriber Role
Subscribers can only log in to your WordPress site, update their user profiles, and change their passwords. They can’t write posts, view comments, or do anything else inside your WordPress admin area.
This user role is particularly useful if you have a membership site, online store, or another site where users can register and log in.
The default WordPress user roles have capabilities that will work well for most WordPress websites and blogs.
For example, if you run a magazine website, then the editor role can be assigned to senior staff, the author role can be for junior staff, and the contributor role can be for guest writers.
But sometimes you might want to customize the permissions and add new capabilities assigned to the role for the specific needs of your website.
How to Define Custom User Roles in WordPress
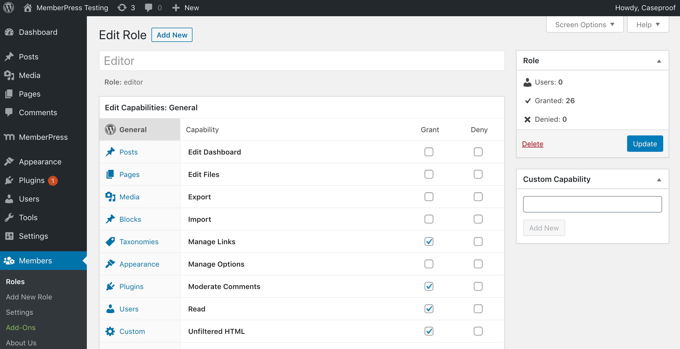
To define custom user roles in WordPress, you will usually need a user role editor plugin like Members. This plugin allows you to add or remove capabilities from user roles in WordPress.
Besides adding new roles for specific functions, this plugin lets you edit existing user permissions.
For example, you may wish to limit authors to their own posts in WordPress admin or not allow authors to publish posts.
Some plugins like WooCommerce will also add a new user role by default, like Shop Manager. This role gives users the ability to manage the shop without granting them full control over the entire website, which would be the case with the Administrator role.
Additionally, you can also install a custom user role plugin for specific permissions.
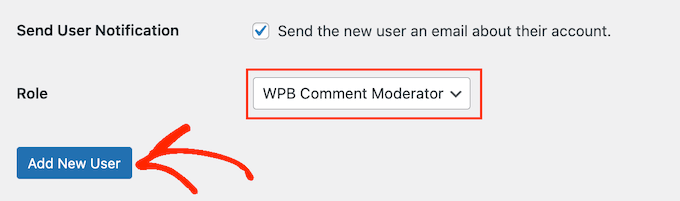
For example, with the Comment Moderation Role by WPBeginner plugin, you can create a user role specifically to moderate comments and nothing else.
How to Restrict Content Based on User Role
On some sites, you may want specific users to be able to access restricted content. For example, you might want to create a membership site and only allow paying members to access your courses, videos, or other premium content.
It used to be that creating a membership website took a long time, and required a lot of work. Back then, you had to figure out how to manage users, set up memberships, decide how to receive payments, and more.
Thankfully, there are some impressive membership plugins for WordPress that make setting up your membership site super easy.
One of the most popular WordPress membership plugins is MemberPress. It has a powerful set of features that makes setting up a membership site a breeze.
You can use the MemberPress plugin to add different membership plans, set up pricing, create custom user accounts, and more.
This WordPress plugin also has built-in support for PayPal and Stripe payment gateways, so your members can make secure payments online.
You can see our guide to creating a WordPress membership site for step-by-step instructions.
We hope this article helped you learn more about user roles in WordPress. You may also want to see our Additional Reading list below for related articles on useful WordPress tips, tricks, and ideas.
If you liked this article, then please subscribe to our YouTube Channel for WordPress video tutorials. You can also find us on Twitter and Facebook.




